NFkB p50 Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab207217)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Semi-quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 3 hr 30 min
- Sample type: Cell Lysate, Nuclear Extracts
- Sensitivity: 500 ng/well
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 1 x 96 tests 5 x 96 tests 10X Antibody Binding Buffer 1 x 2.2ml 1 x 11ml 10X Wash Buffer 1 x 22ml 1 x 110ml 96-well NFkB assay plate 1 unit 5 units Anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated IgG (0.25 μg/μL) 1 x 11µl 1 x 55µl Binding Buffer 1 x 10ml 1 x 50ml Developing Solution 1 x 11ml 1 x 55ml Dithiothreitol (DTT) (1 M) 1 x 100µl 1 x 500µl Herring sperm DNA (1 μg/μL) 1 x 100µl 1 x 500µl Lysis Buffer 1 x 10ml 1 x 50ml Mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/µL) 1 x 100µl 1 x 500µl NFkB p50 antibodies 1 x 11µl 1 x 55µl Plate sealer 1 unit 5 units Positive control nuclear extract 1 x 40µl 1 x 200µl Protease Inhibitor Cocktail 1 x 100µl 1 x 500µl Stop Solution 1 x 11ml 1 x 55ml Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/µL) 1 x 100µl 1 x 500µl -
Research areas
-
Function
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105. -
Sequence similarities
Contains 7 ANK repeats.
Contains 1 death domain.
Contains 1 RHD (Rel-like) domain. -
Domain
The C-terminus of p105 might be involved in cytoplasmic retention, inhibition of DNA-binding, and transcription activation.
Glycine-rich region (GRR) appears to be a critical element in the generation of p50. -
Post-translational
modificationsWhile translation occurs, the particular unfolded structure after the GRR repeat promotes the generation of p50 making it an acceptable substrate for the proteasome. This process is known as cotranslational processing. The processed form is active and the unprocessed form acts as an inhibitor (I kappa B-like), being able to form cytosolic complexes with NF-kappa B, trapping it in the cytoplasm. Complete folding of the region downstream of the GRR repeat precludes processing.
Phosphorylation at 'Ser-903' and 'Ser-907' primes p105 for proteolytic processing in response to TNF-alpha stimulation. Phosphorylation at 'Ser-927' and 'Ser-932' are required for BTRC/BTRCP-mediated proteolysis.
Polyubiquitination seems to allow p105 processing.
S-nitrosylation of Cys-61 affects DNA binding. -
Cellular localization
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- DKFZp686C01211
- DNA binding factor KBF1
- DNA binding factor KBF1 EBP1
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 4790 Human
- Entrez Gene: 18033 Mouse
- Omim: 164011 Human
- SwissProt: P19838 Human
- SwissProt: P25799 Mouse
- Unigene: 618430 Human
- Unigene: 256765 Mouse
Images
-
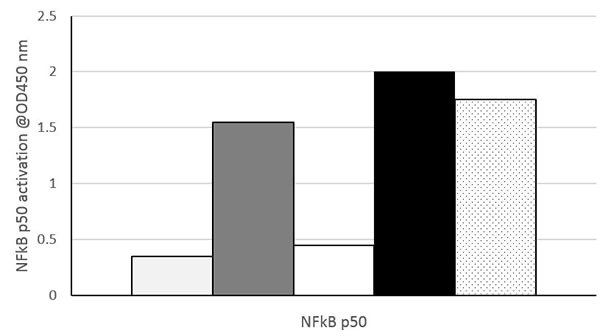
Nuclear extracts prepared from untreated HeLa cells (Light gray), HeLa cells treated with TNF-α (Dark gray), untreated Jurkat cells (White), Jurkat cells treated with PMA and calcium ionophore (CI) (Black) and Raji cells (Black dots on white) were assayed at 10 µg/well for NFkB p50 activity using ab207217. Data shown are the results from wells assayed in duplicate. These results are provided for demonstration only.