Human Parkin ELISA Kit (ab212159)
Key features and details
- One-wash 90 minute protocol
- Sensitivity: 9.7 pg/ml
- Range: 46.88 pg/ml - 3000 pg/ml
- Sample type: Cell culture extracts, Tissue Extracts
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Assay type: Sandwich (quantitative)
- Reacts with: Human
Overview
-
Product name
Human Parkin ELISA Kit
See all Parkin kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Precision
Intra-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Overall 5 3% Inter-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Overall 3 6% -
Sample type
Cell culture extracts, Tissue Extracts -
Assay type
Sandwich (quantitative) -
Sensitivity
9.7 pg/ml -
Range
46.88 pg/ml - 3000 pg/ml -
Recovery
Sample specific recovery Sample type Average % Range Cell culture extracts 106 103% - 108% -
Assay time
1h 30m -
Assay duration
One step assay -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human -
Product overview
Human Parkin ELISA Kit (ab212159) is a single-wash 90 min sandwich ELISA designed for the quantitative measurement of Parkin protein in cell culture extracts and tissue extracts. It uses our proprietary SimpleStep ELISA® technology. Quantitate Human Parkin with 9.7 pg/ml sensitivity.
SimpleStep ELISA® technology employs capture antibodies conjugated to an affinity tag that is recognized by the monoclonal antibody used to coat our SimpleStep ELISA® plates. This approach to sandwich ELISA allows the formation of the antibody-analyte sandwich complex in a single step, significantly reducing assay time. See the SimpleStep ELISA® protocol summary in the image section for further details. Our SimpleStep ELISA® technology provides several benefits:
- Single-wash protocol reduces assay time to 90 minutes or less
- High sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility from superior antibodies
- Fully validated in biological samples
- 96-wells plate breakable into 12 x 8 wells stripsA 384-well SimpleStep ELISA® microplate (ab203359) is available to use as an alternative to the 96-well microplate provided with SimpleStep ELISA® kits.
-
Notes
Parkin functions within a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins. This way, Parkin participates in the removal and/or detoxification of abnormally folded or damaged protein via proteasome pathway by mediating 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of misfolded proteins including PARK7 and 22 kDa O-linked glycosylated isoform of SNCAIP. Parkin also mediates monoubiquitination of BCL2, thereby acting as a positive regulator of autophagy. Parkin also promotes the autophagic degradation of dysfunctional depolarized mitochondria (mitophagy) by promoting the ubiquitination of mitochondrial proteins such as TOMM20, RHOT1/MIRO1 and USP30. Parkin also mediates polyubiquitination of ZNF746, followed by degradation of ZNF746 by the proteasome; possibly playing a role in the regulation of neuron death.
Abcam has not and does not intend to apply for the REACH Authorisation of customers’ uses of products that contain European Authorisation list (Annex XIV) substances.
It is the responsibility of our customers to check the necessity of application of REACH Authorisation, and any other relevant authorisations, for their intended uses. -
Platform
Pre-coated microplate (12 x 8 well strips)
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at +4°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 1 x 96 tests 10X Human Parkin Capture Antibody 1 x 600µl 10X Human Parkin Detector Antibody 1 x 600µl 10X Wash Buffer PT (ab206977) 1 x 20ml 50X Cell Extraction Enhancer Solution (ab193971) 1 x 1ml 5X Cell Extraction Buffer PTR (ab193970) 1 x 10ml Antibody Diluent 5BI 1 x 6ml Human Parkin Lyophilized Recombinant Protein 2 vials Plate Seals 1 unit Sample Diluent NS (ab193972) 1 x 12ml SimpleStep Pre-Coated 96-Well Microplate (ab206978) 1 unit Stop Solution 1 x 12ml TMB Development Solution 1 x 12ml -
Research areas
-
Function
Functions within a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins, such as BCL2, SYT11, CCNE1, GPR37, STUB1, a 22 kDa O-linked glycosylated isoform of SNCAIP, SEPT5, ZNF746 and AIMP2. Mediates monoubiquitination as well as 'Lys-48'-linked and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of substrates depending on the context. Participates in the removal and/or detoxification of abnormally folded or damaged protein by mediating 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of misfolded proteins such as PARK7: 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitinated misfolded proteins are then recognized by HDAC6, leading to their recruitment to aggresomes, followed by degradation. Mediates 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of SNCAIP, possibly playing a role in Lewy-body formation. Mediates monoubiquitination of BCL2, thereby acting as a positive regulator of autophagy. Promotes the autophagic degradation of dysfunctional depolarized mitochondria. Mediates 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of ZNF746, followed by degradation of ZNF746 by the proteasome; possibly playing a role in role in regulation of neuron death. Limits the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Loss of this ubiquitin ligase activity appears to be the mechanism underlying pathogenesis of PARK2. May protect neurons against alpha synuclein toxicity, proteasomal dysfunction, GPR37 accumulation, and kainate-induced excitotoxicity. May play a role in controlling neurotransmitter trafficking at the presynaptic terminal and in calcium-dependent exocytosis. Regulates cyclin-E during neuronal apoptosis. May represent a tumor suppressor gene. -
Tissue specificity
Highly expressed in the brain including the substantia nigra. Expressed in heart, testis and skeletal muscle. Expression is down-regulated or absent in tumor biopsies, and absent in the brain of PARK2 patients. Overexpression protects dopamine neurons from kainate-mediated apoptosis. Found in serum (at protein level). -
Pathway
Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in PARK2 are a cause of Parkinson disease (PARK) [MIM:168600]. A complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscular rigidity and postural instability. Additional features are characteristic postural abnormalities, dysautonomia, dystonic cramps, and dementia. The pathology of Parkinson disease involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the presence of Lewy bodies (intraneuronal accumulations of aggregated proteins), in surviving neurons in various areas of the brain. The disease is progressive and usually manifests after the age of 50 years, although early-onset cases (before 50 years) are known. The majority of the cases are sporadic suggesting a multifactorial etiology based on environmental and genetic factors. However, some patients present with a positive family history for the disease. Familial forms of the disease usually begin at earlier ages and are associated with atypical clinical features.
Defects in PARK2 are the cause of Parkinson disease type 2 (PARK2) [MIM:600116]; also known as early-onset parkinsonism with diurnal fluctuation (EPDF) or autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinson disease (PDJ). A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, tremor, and onset usually befor 40. It differs from classic Parkinson disease by early DOPA-induced dyskinesia, diurnal fluctuation of the symptoms, sleep benefit, dystonia and hyper-reflexia. Dementia is absent. Pathologically, patients show loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, similar to that seen in Parkinson disease; however, Lewy bodies (intraneuronal accumulations of aggregated proteins) are absent.
Note=Defects in PARK2 may be involved in the development and/or progression of ovarian cancer. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the RBR family. Parkin subfamily.
Contains 1 IBR-type zinc finger.
Contains 2 RING-type zinc fingers.
Contains 1 ubiquitin-like domain. -
Domain
The ubiquitin-like domain binds the PSMD4 subunit of 26S proteasomes. -
Post-translational
modificationsAuto-ubiquitinates in an E2-dependent manner leading to its own degradation. Also polyubiquitinated by RNF41 for proteasomal degradation.
S-nitrosylated. The inhibition of PARK2 ubiquitin E3 ligase activity by S-nitrosylation could contribute to the degenerative process in PD by impairing the ubiquitination of PARK2 substrates. -
Cellular localization
Cytoplasm > cytosol. Nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion. Mainly localizes in the cytosol. Co-localizes with SYT11 in neutrites. Co-localizes with SNCAIP in brainstem Lewy bodies. Relocates to dysfunctional mitochondria that have lost the mitochondial membrane potential; recruitement to mitochondria is PINK1-dependent. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- AR JP
- E3 ubiquitin ligase
- E3 ubiquitin protein ligase parkin
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 5071 Human
- Omim: 602544 Human
- SwissProt: O60260 Human
- Unigene: 132954 Human
Images
-
SimpleStep ELISA technology allows the formation of the antibody-antigen complex in one single step, reducing assay time to 90 minutes. Add samples or standards and antibody mix to wells all at once, incubate, wash, and add your final substrate. See protocol for a detailed step-by-step guide.
-
Background-subtracted data values (mean +/- SD) are graphed.
-
 Interpolated concentrations of Parkin in extract of HEK293T cells overexpressing Parkin samples based on a 2.5 µg/mL extract load.
Interpolated concentrations of Parkin in extract of HEK293T cells overexpressing Parkin samples based on a 2.5 µg/mL extract load.The concentrations of Parkin were measured in duplicate and interpolated from the Parkin standard curve and corrected for sample dilution. The interpolated dilution factor corrected values are plotted (mean +/- SD, n=2). The mean Parkin concentration was determined to be 2,180 pg/mL in Parkin overexpression extract.
-
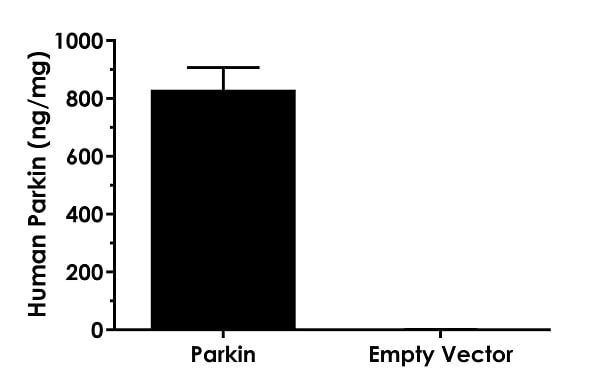 Interpolated concentrations of Parkin in extracts of HEK293T cells overexpressing Parkin and HEK293T cells transfected with the associated empty vector.
Interpolated concentrations of Parkin in extracts of HEK293T cells overexpressing Parkin and HEK293T cells transfected with the associated empty vector.The concentrations of Parkin were measured in three different dilutions in duplicate and interpolated from the Parkin standard curve and corrected for sample dilution. The interpolated dilution factor corrected values are plotted in ng Parkin per mg of extract (mean +/- SD, n=3). Parkin concentration was determined to be 830 ng/mg in extract of HEK293T cells overexpressing Parkin, and 1 ng/mg in extract of HEK293T cells transfected with the empty vector.
-
To learn more about the advantages of recombinant antibodies see here.















