H89 dihydrochloride, Kinase inhibitor (ab120341)
Key features and details
- Kinase inhibitor
- CAS Number: 130964-39-5
- Purity: > 98%
- Soluble in DMSO to 100 mM and in water to 25 mM (with heating)
- Form / State: Solid
- Source: Synthetic
Overview
-
Product name
H89 dihydrochloride, Kinase inhibitor -
Description
Kinase inhibitor -
Biological description
Kinase inhibitor, commonly used as a protein kinase A inhibitor (IC50 = 135 nM). Also inhibits other kinases, including MSK1 , S6K1 and ROCKII (IC50 values are 120, 80 and 270 nM, respectively).
-
Purity
> 98% -
CAS Number
130964-39-5 -
Chemical structure

Properties
-
Chemical name
N-[2-[[3-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-propen-1-yl]amino]ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide dihydrochloride -
Molecular weight
519.28 -
Molecular formula
C20H20BrN3O2S.2HCl -
PubChem identifier
5702541 -
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Store under desiccating conditions. The product can be stored for up to 12 months. -
Solubility overview
Soluble in DMSO to 100 mM and in water to 25 mM (with heating) -
Handling
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20°C. Generally, these will be useable for up to one month. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Refer to SDS for further information.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please visit our frequently asked questions (FAQ) page for more details.
-
SMILES
C1=CC2=C(C=CN=C2)C(=C1)S(=O)(=O)NCCNC/C=C/C3=CC=C(C=C3)Br.Cl.Cl -
Source
Synthetic
-
Research areas
- Biochemicals
- Pharmacology
- Signaling
- Signal transduction
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Metabolism
- Pathways and Processes
- Metabolic signaling pathways
- Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism
- Lipid metabolism
- Metabolism
- Pathways and Processes
- Metabolic signaling pathways
- Energy transfer pathways
- Integration of energy
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Heart disease
- Signaling
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Pain & inflammation
- Signaling
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Signaling
- Signal transduction
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Diabetes
- Signaling
- Signal transduction
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Hypertension
- Signaling
- Signal transduction
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Obesity
- Signaling
- Signal transduction
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
- Biochemicals
- Research Area
- Respiratory disease
- Signaling
- Inositol & cAMP signaling
- Protein Kinase A
- Inhibitors
Images
-
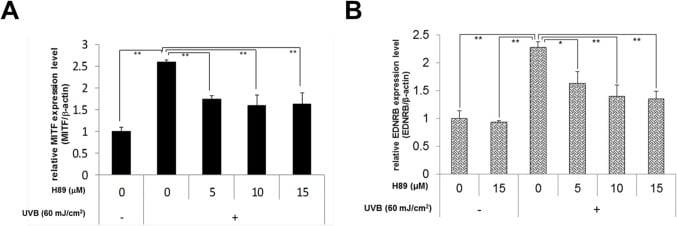 Functional Studies - H89 dihydrochloride, Kinase inhibitor (ab120341) Image from Tagashira, Hideki et al., PLOS One., 10(6):e0128678. Fig 8.; doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128678. Reproduced under the Creative Commons license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Functional Studies - H89 dihydrochloride, Kinase inhibitor (ab120341) Image from Tagashira, Hideki et al., PLOS One., 10(6):e0128678. Fig 8.; doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128678. Reproduced under the Creative Commons license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/Normal human melanocytes (NHMs) were treated with ab120341 at the indicated concentrations to test if the inhibition of MSK1 activation results in the down-regulated MITF and EDNRB expression in UVB-exposed NHMs. ab120341 was added immediately after UVB irradiation and cells were cultured for 6h (for MITF, A) or 24 h (for EDNRB, B). Total mRNAs were purified and Real-time RT-PCR was carried out with MITF or EDNRB primer and β-actin primer as the internal control. Error bars represent S.D. from triplicate experiments. *P
Tagashira, Hideki et al., PLOS One., 10(6):e0128678. Fig 8.; doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128678.






