ADP Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab211087)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Quantitative
- Detection method: Fluorescent
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Sample type: Cell Lysate, Tissue Lysate
- Sensitivity: 0.05 µM
Overview
-
Product name
ADP Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
See all ADP kits -
Detection method
Fluorescent -
Sample type
Cell Lysate, Tissue Lysate -
Assay type
Quantitative -
Sensitivity
0.05 µM -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mammals, Other species -
Product overview
ADP Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab211087) provides a sensitive fluorescence method to detect ADP in cell and tissue lysates. This assay is particularly suitable for detecting ADP in samples that contain reducing substances, which may interfere with oxidase-based assays. In this assay, ADP, in the presence of ADP Enzyme Mix is converted to an intermediate, which reacts with the fluorescent probe to generate a strong stable signal at Ex/Em = 535/587 nm. This kit can detect as low as 10 pmol or 0.05 µM of ADP in samples.
-
Notes
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is an organic molecule that plays a critical role in cellular metabolism and energy transfer reactions. ADP is a product of ATP dephosphorylation and it can be rephosphorylated to ATP. These dephosphorylations and rephosphorylations occur via various phosphorylases and kinases. ADP is stored in platelets and can be released to interact with variety of purinergic receptors. ADP levels regulate several enzymes involved in intermediary metabolism. ADP conversion to ATP primarily occurs within the mitochondrion and chloroplast although several such processes also occur in the cytoplasm.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 100 tests ADP Assay Buffer 1 x 25ml ADP Developer (10 U) 1 vial ADP Enzyme Mix I (10 U) 1 vial ADP Enzyme Mix II (30 U) 1 vial ADP Standard (1 µmole) 1 vial PicoProbe (in DMSO) 1 x 400µl -
Research areas
-
Relevance
ADP (Adenosine diphosphate) is a product of ATP dephosphorylation and it can be rephosphorylated to ATP. Dephosphorylation and rephosphorylation occur via various phosphatases, phosphorylases and kinases. ADP is stored in platelets and can be released to interact with a variety of purinergic receptors. ADP levels regulate several enzymes involved in intermediary metabolism. ADP conversion to ATP primarily occurs within the mitochondrion and chloroplast although several such processes occur in the cytoplasm. -
Alternative names
- Adenosine diphosphate
Images
-
Typical ADP standard calibration curve.
-
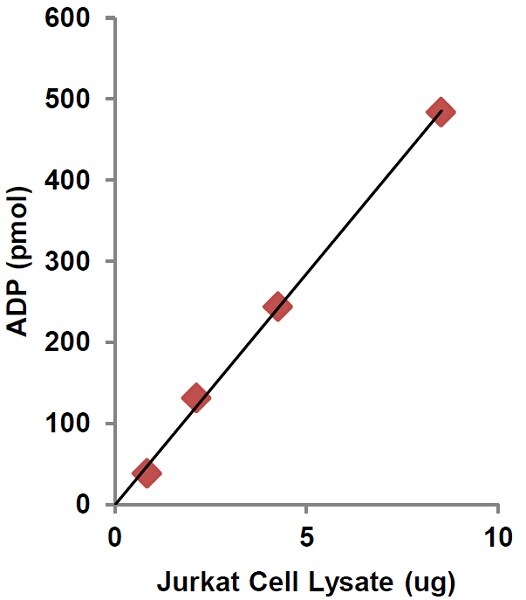
Measurement of ADP in Jurkat cell lysates (increasing protein concentration 1–10 µg).
-
Measurement of ADP in Jurkat and HeLa cell lysate (2 µg).