Anti-PUMA antibody (ab9645)
Key features and details
- Rabbit polyclonal to PUMA
- Suitable for: WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype: IgG
Overview
-
Product name
Anti-PUMA antibody
See all PUMA primary antibodies -
Description
Rabbit polyclonal to PUMA -
Host species
Rabbit -
Specificity
Specific to PUMA alpha -
Tested applications
Suitable for: WB, ICC/IF, IHC-Pmore details -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human
Predicted to work with: Mouse, Rat
-
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide:
ARARQEGSSPEPVEG
, corresponding to amino acids 2-16 of Human PUMA. (Peptide available as ab9646). -
Positive control
- WB: K562 lysate IHC-P: Human breast carcinoma sections ICC/IF: K562 cells
-
General notes
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse (1-3). PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b (1). PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis.
Properties
-
Form
Liquid -
Storage instructions
Shipped at 4°C. Upon delivery aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles. -
Storage buffer
pH: 7.2
Preservative: 0.02% Sodium azide -
 Concentration information loading...
Concentration information loading... -
Purity
Immunogen affinity purified -
Primary antibody notes
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse (1-3). PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b (1). PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. -
Clonality
Polyclonal -
Isotype
IgG -
Research areas
Images
-
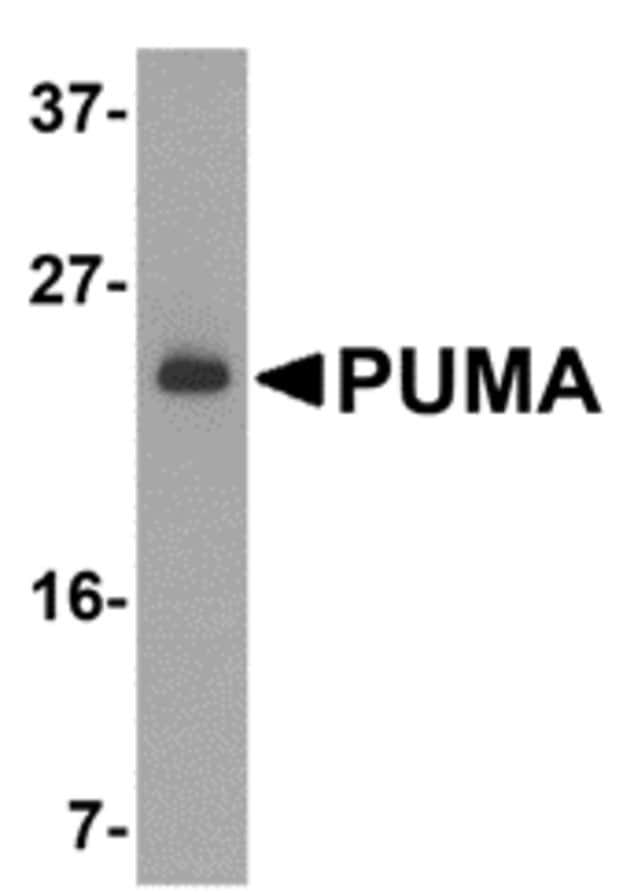
Anti-PUMA antibody (ab9645) at 2 µg/ml + K562 cell lysates at 15 µg
Secondary
Goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP conjugate at 1/10000 dilutionPrimary incubation: 1 hour at room temperature in 5% NFDM/TBST.
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue labeling PUMA with ab9645 at 10 μg/mL. Sections were fixed with formaldehyde and blocked with 10% serum for 1 hour at room temperature. Antigen retrieval was by heat mediation with a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Samples were incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4˚C. A goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) at 1/250 was used as secondary. Counter stained with Hematoxylin.
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast tissue labeling PUMA with ab9645 at 2.5 μg/mL. Sections were fixed with formaldehyde and blocked with 10% serum for 1 hour at room temperature. Antigen retrieval was by heat mediation with a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Samples were incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4˚C. A goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) at 1/250 was used as secondary. Counter stained with Hematoxylin.
-
Immunofluorescent analysis of 4% paraformaldehydefixed K562 cells labeling PUMA with ab9645 at 20 μg/mL, followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody at 1/500 dilution (red) and DAPI staining (blue).
-
Immunofluorescent analysis of 4% paraformaldehydefixed K562 cells labeling PUMA with ab9645 at 10 μg/mL, followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody at 1/500 dilution (red). Image showing cytosol staining on K562 cells.