Recombinant human Syk protein (ab196062)
Key features and details
- Expression system: Baculovirus infected Sf9 cells
- Purity: >= 60% SDS-PAGE
- Active: Yes
- Tags: GST tag N-Terminus
- Suitable for: SDS-PAGE, Functional Studies
-
Product name
Recombinant human Syk protein
See all Syk proteins and peptides -
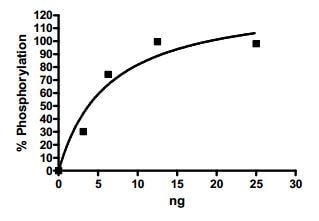
Biological activity
Specific activity: 139 pmol/min/μg.
SYK was incubated with a substrate for 1 hour at RT in 1X kinase buffer supplemented with ATP. Developer solution was added to reaction and reaction was stopped after 1 hour of incubation at RT.
-
Purity
>= 60 % SDS-PAGE. -
Expression system
Baculovirus infected Sf9 cells -
Accession
-
Protein length
Protein fragment -
Animal free
No -
Nature
Recombinant -
-
Species
Human -
Sequence
RPKEVYLDRKLLTLEDKELGSGNFGTVKKGYYQMKKVVKTVAVKILKNEA NDPALKDELLAEANVMQQLDNPYIVRMIGICEAESWMLVMEMAELGPLNK YLQQNRHVKDKNIIELVHQVSMGMKYLEESNFVHRDLAARNVLLVTQHYA KISDFGLSKALRADENYYKAQTHGKWPVKWYAPECINYYKFSSKSDVWSF GVLMWEAFSYGQKPYRGMKGSEVTAMLEKGERMGCPAGCPREMYDLMNLC WTYDVENRPGFAAVELRLRNYYYDVVN -
Predicted molecular weight
58 kDa including tags -
Amino acids
359 to 635 -
Tags
GST tag N-Terminus -
Additional sequence information
NM_003177.
-
Preparation and Storage
-
Alternative names
- EC 2.7.10.2
- kinase Syk
- KSYK
see all -
Function
Non-receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates signal transduction downstream of a variety of transmembrane receptors including classical immunoreceptors like the B-cell receptor (BCR). Regulates several biological processes including innate and adaptive immunity, cell adhesion, osteoclast maturation, platelet activation and vascular development. Assembles into signaling complexes with activated receptors at the plasma membrane via interaction between its SH2 domains and the receptor tyrosine-phosphorylated ITAM domains. The association with the receptor can also be indirect and mediated by adapter proteins containing ITAM or partial hemITAM domains. The phosphorylation of the ITAM domains is generally mediated by SRC subfamily kinases upon engagement of the receptor. More rarely signal transduction via SYK could be ITAM-independent. Direct downstream effectors phosphorylated by SYK include VAV1, PLCG1, PI-3-kinase, LCP2 and BLNK. Initially identified as essential in B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, it is necessary for the maturation of B-cells most probably at the pro-B to pre-B transition. Activated upon BCR engagement, it phosphorylates and activates BLNK an adapter linking the activated BCR to downstream signaling adapters and effectors. It also phosphorylates and activates PLCG1 and the PKC signaling pathway. It also phosphorylates BTK and regulates its activity in B-cell antigen receptor (BCR)-coupled signaling. In addition to its function downstream of BCR plays also a role in T-cell receptor signaling. Plays also a crucial role in the innate immune response to fungal, bacterial and viral pathogens. It is for instance activated by the membrane lectin CLEC7A. Upon stimulation by fungal proteins, CLEC7A together with SYK activates immune cells inducing the production of ROS. Also activates the inflammasome and NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription of chemokines and cytokines in presence of pathogens. Regulates neutrophil degranulation and phagocytosis through activation of the MAPK signaling cascade. Also mediates the activation of dendritic cells by cell necrosis stimuli. Also involved in mast cells activation. Also functions downstream of receptors mediating cell adhesion. Relays for instance, integrin-mediated neutrophils and macrophages activation and P-selectin receptor/SELPG-mediated recruitment of leukocytes to inflammatory loci. Plays also a role in non-immune processes. It is for instance involved in vascular development where it may regulate blood and lymphatic vascular separation. It is also required for osteoclast development and function. Functions in the activation of platelets by collagen, mediating PLCG2 phosphorylation and activation. May be coupled to the collagen receptor by the ITAM domain-containing FCER1G. Also activated by the membrane lectin CLEC1B that is required for activation of platelets by PDPN/podoplanin. Involved in platelet adhesion being activated by ITGB3 engaged by fibrinogen. -
Tissue specificity
Widely expressed in hematopoietic cells (at protein level). Within the B-cells compartment it is for instance expressed for pro-B-cells to plasma cells. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. SYK/ZAP-70 subfamily.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Contains 2 SH2 domains. -
Domain
The SH2 domains mediate the interaction of SYK with the phosphorylated ITAM domains of transmembrane proteins. Some proteins like CLEC1B have a partial ITAM domain (also called hemITAM) containing a single YxxL motif. The interaction with SYK requires CLEC1B homodimerization. -
Post-translational
modificationsUbiquitinated by CBLB after BCR activation; which promotes proteasomal degradation.
Autophosphorylated. Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by LYN following receptors engagement. Phosphorylation on Tyr-323 creates a binding site for CBL, an adapter protein that serves as a negative regulator of BCR-stimulated calcium ion signaling. Phosphorylation at Tyr-348 creates a binding site for VAV1. Phosphorylation on Tyr-348 and Tyr-352 enhances the phosphorylation and activation of phospholipase C-gamma and the early phase of calcium ion mobilization via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-independent pathway (By similarity). Phosphorylation on Ser-297 is very common, it peaks 5 minutes after BCR stimulation, and creates a binding site for YWHAG. Phosphorylation at Tyr-630 creates a binding site for BLNK. Dephosphorylated by PTPN6. -
Cellular localization
Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytosol. - Information by UniProt