Recombinant human CD127 protein (Fc Chimera Active) (ab174078)
Key features and details
- Expression system: HEK 293 cells
- Purity: > 95% SDS-PAGE
- Endotoxin level:
- Active: Yes
- Suitable for: Functional Studies, SDS-PAGE
Preparation and Storage
-
Alternative names
- CD 127
- CD127
- CD127 antigen
see all -
Function
Receptor for interleukin-7. Also acts as a receptor for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). -
Involvement in disease
Defects in IL7R are a cause of severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell-positive/NK-cell-positive (T(-)B(+)NK(+) SCID) [MIM:608971]. A form of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. Patients present in infancy recurrent, persistent infections by opportunistic organisms. The common characteristic of all types of SCID is absence of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity due to a defect in T-cell development.
Genetic variations in IL7R are a cause of susceptibility to multiple sclerosis type 3 (MS3) [MIM:612595]. A multifactorial, inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Sclerotic lesions are characterized by perivascular infiltration of monocytes and lymphocytes and appear as indurated areas in pathologic specimens (sclerosis in plaques). The pathological mechanism is regarded as an autoimmune attack of the myelin sheat, mediated by both cellular and humoral immunity. Clinical manifestations include visual loss, extra-ocular movement disorders, paresthesias, loss of sensation, weakness, dysarthria, spasticity, ataxia and bladder dysfunction. Genetic and environmental factors influence susceptibility to the disease. Note=A polymorphism at position 244 strongly influences susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Overtransmission of the major 'C' allele coding for Thr-244 is detected in offspring affected with multiple sclerosis. In vitro analysis of transcripts from minigenes containing either 'C' allele (Thr-244) or 'T' allele (Ile-244) shows that the 'C' allele results in an approximately two-fold increase in the skipping of exon 6, leading to increased production of a soluble form of IL7R. Thus, the multiple sclerosis associated 'C' risk allele of IL7R would probably decrease membrane-bound expression of IL7R. As this risk allele is common in the general population, some additional triggers are probably required for the development and progression of MS. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family. Type 4 subfamily.
Contains 1 fibronectin type-III domain. -
Domain
The WSXWS motif appears to be necessary for proper protein folding and thereby efficient intracellular transport and cell-surface receptor binding.
The box 1 motif is required for JAK interaction and/or activation. -
Post-translational
modificationsN-glycosylated IL-7Ralpha binds IL7 300-fold more tightly than the unglycosylated form. -
Cellular localization
Secreted and Cell membrane. - Information by UniProt
Images
-
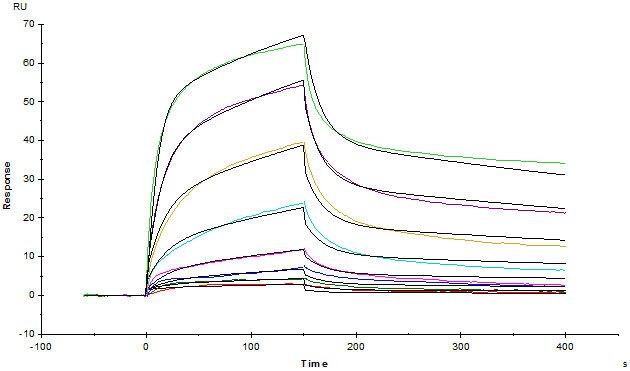
Captured Human IL-7 R alpha, Fc Tag (ab174078) on CM5 chip via anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind Human IL-7, Tag Free (ab155728) with an affinity constant of 23.9 nM as determined in a SPR assay
-
Immobilized ActiveMax® Human IL-7, Tag Free (ab155728) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human IL-7 R alpha, Fc Tag (ab174078) with a linear range of 1-16 ng/mL
-
SDS-PAGE analysis of ab174078 purity