HNF (HNF1, HNF3alpha, HNF3beta, HNF4alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab207208)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Semi-quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 3 hr 30 min
- Sample type: Nuclear Extracts
- Sensitivity: 500 ng/well
Overview
-
Product name
HNF (HNF1, HNF3alpha, HNF3beta, HNF4alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Nuclear Extracts -
Assay type
Semi-quantitative -
Sensitivity
500 ng/well -
Assay time
3h 30m -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mouse, Rat, Human -
Product overview
HNF (HNF1, HNF3alpha, HNF3beta, HNF4alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab207208) is a high throughput assay to quantify activation of HNF family members at the same time. This assay combines a quick ELISA format with a sensitive and specific non-radioactive assay for transcription factor activation.
Specific double stranded DNA sequences containing the HNF consensus binding sites [HNF1 (5´–GTTAATGATTAAC–3´), HNF3 (5´–GATTATTGACTT–3´) and HNF4 (5´–TGGACTTAG–3´)] has been immobilized onto a 96-well plate. Active HNF present in the nuclear extract specifically binds to the oligonucleotide mixture. HNF is detected by a primary antibody that recognizes an epitope of HNF accessible only when the protein is activated and bound to its target DNA. An HRP-conjugated secondary antibody provides sensitive colorimetric readout at OD 450 nm. This product detects human, mouse and rat HNF.
Key performance and benefits:
- Assay time: 3.5 hours (cell extracts preparation not included).
- Detection limit:
- Detection range: 0.5 – 5 µg nuclear extract/well.
-
Notes
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factors (HNFs), though originally discovered in the liver, are distinct transcription factors belonging to several families and involved in a wide variety of biological pathways. To date, several different HNFs have been described: HNF1α and β, HNF3α, β and γ, HNF4α and HNF6α and β. Although all are important in liver development and function, HNFs are also found in other tissues such as the kidney, spleen, thymus and pancreas.
HNF1 is a member of the homeodomain family. The N-terminus contains a dimerization domain allowing for homo- or heterodimerization. HNF1 plays a crucial role in liver development during embryogenesis and metabolism homeostasis in the adult. It helps regulate such genes as glucose-cotransporter-2 in the kidney, phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) in the liver and insulin, L-pyruvate kinase and aldolase B in pancreatic B cells. HNF3α, β and γ are members of the winged-helix/forkhead DNA binding domain family. They are found in the liver, pancreas, intestine and lung. HNF3 target genes include albumin, Apo B, transferrin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1, aldolase B and complement protein C. HNF4 is a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily, similar to RXR. It is found in the liver, kidney, intestine and pancreas. It regulates genes such as apoA-I, apoA-II and apoB for lipid metabolism, insulin, pyruvate kinase and dehydrogenase for protein metabolism, and factors VII, IX, X and fibrinogen for blood coagulation. It also regulates the expression of HNF1. HNF6 is the prototype of the novel ONECUT class of cut-homeoproteins, characterized by the presence of a single cut domain. It is present in the liver, brain, spleen, pancreas and testis. It controls genes coding for 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (involved in glucose metabolism), CYP2C12 (involved in steroid metabolism), transthyretin (involved in plasma transport) and protein C (controls blood coagulation). HNF6 also regulates the expression of HNF3β and 4.
In addition, mutations in HNF genes have been shown to lead to Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY), which is characterized by an autosomal dominant inheritance, an early age onset and abnormal pancreatic B-cell function. MODY1 represents mutations in HNF4α, MODY3 represents mutations in HNF1β and MODY5 represents mutations in HNF1β. It has also been proposed that HNF3β is involved in late-onset type II diabetes, but there is no clear evidence to support this theory. The most common form is MODY3, accounting for about 60% of cases. In all forms of MODY, insulin levels are affected by defective secretions of pancreatic B-cells.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 2 x 96 tests 10X Antibody Binding Buffer 2 x 2.2ml 10X Wash Buffer 1 x 60ml 96-well HNF family assay plate 2 units Anti-goat HRP-conjugated antibody 1 x 11µl Anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated IgG (0.25 μg/μL) 1 x 11µl Binding Buffer 1 x 10ml Developing Solution 2 x 11ml Dithiothreitol (DTT) (1 M) 1 x 100µl Hep G2 nuclear extract (2.5 μg/μL) 2 x 40µl HNF 1 antibodies 1 x 11µl HNF 3α antibodies 1 x 11µl HNF 3β antibodies 1 x 11µl HNF 4α antibodies 1 x 11µl Lysis Buffer 1 x 10ml Mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl Plate sealer 2 units Protease Inhibitor Cocktail 1 x 100µl Stop Solution 1 x 60ml Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl -
Research areas
-
Function
Transcriptional activator that regulates the tissue specific expression of multiple genes, especially in pancreatic islet cells and in liver. Required for the expression of several liver specific genes. Binds to the inverted palindrome 5'-GTTAATNATTAAC-3'. -
Tissue specificity
Liver. -
Involvement in disease
Hepatic adenomas familial
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 3
Diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent, 20 -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the HNF1 homeobox family.
Contains 1 homeobox DNA-binding domain. -
Cellular localization
Nucleus. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha
- HNF-1-alpha
- HNF-1A
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 6927 Human
- Entrez Gene: 3172 Human
- Entrez Gene: 3169 Human
- Entrez Gene: 3170 Human
- Entrez Gene: 21405 Mouse
- Entrez Gene: 15378 Mouse
- Entrez Gene: 15375 Mouse
- Entrez Gene: 15376 Mouse
see all
Images
-
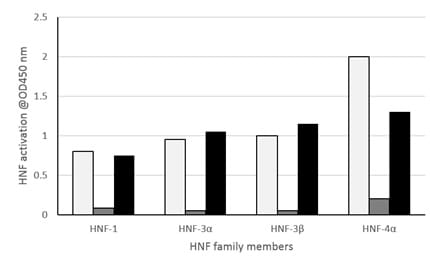 Monitoring HNF family member activation using the ab207208 HNF (1, 3a, 3ß, 4a) T F Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Kit.
Monitoring HNF family member activation using the ab207208 HNF (1, 3a, 3ß, 4a) T F Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Kit.HepG2 nuclear extracts (5 µg/well) were tested for HNF1, HNF3α, HNF3β and HNF4α activation. Activation was monitored in unstimulated nuclear extracts (grey) and in the presence of wild-type (black) or mutated (white) consensus binding oligonucleotides. Note that the wild-type oligonucleotide reduces HNF binding by over 90%, while incubation with the mutant GATA competitor oligo has a limited effect on HNF binding to DNA. These results are provided for demonstration purposes only.


