Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab156064)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Enzyme activity
- Detection method: Fluorescent
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 1 hr
- Sample type: Cell culture extracts, Tissue Extracts
Overview
-
Product name
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) -
Detection method
Fluorescent -
Sample type
Cell culture extracts, Tissue Extracts -
Assay type
Enzyme activity -
Assay time
1h 00m -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human -
Product overview
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) ab156064 detects HDAC activity in lysates.
The HDAC Activity Assay Kit is primarily designed for the evaluation of HDAC inhibitors using a crude HDAC fraction. Also, any cultured primary cell, cell line, or tissue homogenate can be assayed for HDAC activity with the kit if the appropriate dose of HDAC specific inhibitor e.g. Trichostatin A is used.
The HDAC activity assay protocol is based on an acetylated peptide which is conjugated to AMC. AMC is a fluorescent dye and its fluoresence is quenched when conjugated to the peptide. When the HDAC de-acetylates the peptide, it becomes susceptible to cleavage by an enzyme (the Developer component). This then releases free AMC, which can be measured using a fluorescence microplate reader (Ex/Em 355/460 nm).
The HDAC assay has been shown to detect the activity of the HDAC family, at least class I HDACs in Human or animal cell lysates or in column fractions. The assay shows good linearity of sample response. The assay may be used to follow the purification of HDACs or may be used to detect the presence of HDACs in cell lysates.
-
Notes
Applications for this kit include:
1. Monitoring the purification of HDACs including HDAC1, 2, 3 and 8.
2. Screening inhibitors or activators of HDACs.
3. Detecting the effects of pharmacological agents on HDACs.Background information on HDACs
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) are a class of enzymes responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4), allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly.
HDAC proteins occur in four groups (class I, class IIA, class IIB, class III, class IV) based on function and DNA sequence similarity.
Classes I, IIA and IIB are considered "classical" HDACs whose activities are inhibited by trichostatin A (TSA), whereas class III is a family of NAD+-dependent proteins (sirtuins) not affected by TSA. Class IV is considered an atypical class on its own, based solely on DNA sequence similarity to the others. -
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 100 tests Crude HDAC 1 x 500µl Developer 1 x 500µl Fluoro-Deacetylated Peptide (0.2 mM) 1 x 100µl Fluoro-Substrate Peptide (0.2 mM) 1 x 500µl HDAC Assay Buffer 2 x 1ml HDAC Stop Solution 2 x 1ml Trichostatin A (10µM) 1 x 500µl -
Research areas
-
Function
Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Deacetylates SP proteins, SP1 and SP3, and regulates their function. Component of the BRG1-RB1-HDAC1 complex, which negatively regulates the CREST-mediated transcription in resting neurons. Upon calcium stimulation, HDAC1 is released from the complex and CREBBP is recruited, which facilitates transcriptional activation. Deacetylates TSHZ3 and regulates its transcriptional repressor activity. Deacetylates 'Lys-310' in RELA and thereby inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-kappa-B. -
Tissue specificity
Ubiquitous, with higher levels in heart, pancreas and testis, and lower levels in kidney and brain. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the histone deacetylase family. HD type 1 subfamily. -
Post-translational
modificationsSumoylated on Lys-444 and Lys-476; which promotes enzymatic activity. Desumoylated by SENP1.
Phosphorylation on Ser-421 and Ser-423 promotes enzymatic activity and interactions with NuRD and SIN3 complexes.
Ubiquitinated by CHFR, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. -
Cellular localization
Nucleus. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- DKFZp686H12203
- GON 10
- HD1
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 3065 Human
- Omim: 601241 Human
- SwissProt: Q13547 Human
- Unigene: 88556 Human
Images
-
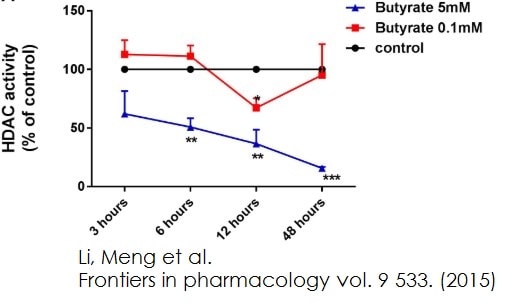 Functional Studies - Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab156064) Li, Meng et al., Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 9 533., Fig 4, doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00533Butyrate, propionate, and TSA inhibited HDACs activity in HUVEC. HDACs activity were inhibited in HUVEC by treatment of butyrate and propionate. The results were normalized using the control as 100%.
Functional Studies - Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab156064) Li, Meng et al., Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 9 533., Fig 4, doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00533Butyrate, propionate, and TSA inhibited HDACs activity in HUVEC. HDACs activity were inhibited in HUVEC by treatment of butyrate and propionate. The results were normalized using the control as 100%. -
8 uL (corresponding to 6.7e6 cells) of nuclear extracts (ab113474) from HL60 cells were assessed kinetically (+/- SD).
-
Different volumes of positive control, with inhibitor (TA), kinetically read (+/- SD).
-
Measurement of HeLa cell endogenous HDAC1 in an immunoprecipitated sample with anti-HDAC1 antibody and following the Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab156064) protocol.
-
Measurement of HeLa cell endogenous HDAC2 in an immunoprecipitated sample with anti-HDAC2 antibody following the Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab156064) protocol.














