Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537)
Key features and details
- Rabbit polyclonal to RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7)
- Suitable for: ELISA, WB, ICC/IF
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype: IgG
Overview
-
Product name
Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody
See all RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS primary antibodies -
Description
Rabbit polyclonal to RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) -
Host species
Rabbit -
Tested applications
Suitable for: ELISA, WB, ICC/IFmore details -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human -
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide corresponding to Human RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS aa 1650-1750 (phospho S7) conjugated to keyhole limpet haemocyanin.
Database link: P24928 -
Positive control
- This antibody gave a positive result when used in the following formaldehyde fixed cell lines: HepG2.
Properties
-
Form
Liquid -
Storage instructions
Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Upon delivery aliquot. Store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. -
Storage buffer
pH: 7.40
Preservative: 0.02% Sodium azide
Constituent: PBS
Batches of this product that have a concentration Concentration information loading...
Concentration information loading...Purity
Immunogen affinity purifiedClonality
PolyclonalIsotype
IgGResearch areas
Associated products
-
Compatible Secondaries
-
Isotype control
-
Recombinant Protein
Applications
Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab126537 in the following tested applications.
The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
Application Abreviews Notes ELISA Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. WB Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 250 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 217 kDa). ICC/IF Use a concentration of 5 µg/ml. Target
-
Function
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Largest and catalytic component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Forms the polymerase active center together with the second largest subunit. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB1 is part of the core element with the central large cleft, the clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft and the jaws that are thought to grab the incoming DNA template. At the start of transcription, a single-stranded DNA template strand of the promoter is positioned within the central active site cleft of Pol II. A bridging helix emanates from RPB1 and crosses the cleft near the catalytic site and is thought to promote translocation of Pol II by acting as a ratchet that moves the RNA-DNA hybrid through the active site by switching from straight to bent conformations at each step of nucleotide addition. During transcription elongation, Pol II moves on the template as the transcript elongates. Elongation is influenced by the phosphorylation status of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II largest subunit (RPB1), which serves as a platform for assembly of factors that regulate transcription initiation, elongation, termination and mRNA processing. Acts as an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase when associated with small delta antigen of Hepatitis delta virus, acting both as a replicate and transcriptase for the viral RNA circular genome. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the RNA polymerase beta' chain family. -
Domain
The C-terminal domain (CTD) serves as a platform for assembly of factors that regulate transcription initiation, elongation, termination and mRNA processing. -
Post-translational
modificationsThe tandem heptapeptide repeats in the C-terminal domain (CTD) can be highly phosphorylated. The phosphorylation activates Pol II. Phosphorylation occurs mainly at residues 'Ser-2' and 'Ser-5' of the heptapeptide repeat and is mediated, at least, by CDK7 and CDK9. CDK7 phosphorylation of POLR2A associated with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Phosphorylation also takes place at 'Ser-7' of the heptapeptide repeat, which is required for efficient transcription of snRNA genes and processing of the transcripts. The phosphorylation state is believed to result from the balanced action of site-specific CTD kinases and phosphatases, and a 'CTD code' that specifies the position of Pol II within the transcription cycle has been proposed. Dephosphorylated by the protein phosphatase CTDSP1.
Among tandem heptapeptide repeats of the C-terminal domain (CTD) some do not match the Y-S-P-T-S-P-S consensus, the seventh serine residue 'Ser-7' being replaced by a lysine. 'Lys-7' in these non-consensus heptapeptide repeats can be alternatively acetylated, methylated and dimethylated. EP300 is one of the enzyme able to acetylate 'Lys-7'. Acetylation at 'Lys-7' of non-consensus heptapeptide repeats is associated with 'Ser-2' phosphorylation and active transcription. It may regulate initiation or early elongation steps of transcription specially for inducible genes.
Methylated at Arg-1810 prior to transcription initiation when the CTD is hypophosphorylated, phosphorylation at Ser-1805 and Ser-1808 preventing this methylation. Symmetrically or asymmetrically dimethylated at Arg-1810 by PRMT5 and CARM1 respectively. Symmetric or asymmetric dimethylation modulates interactions with CTD-binding proteins like SMN1/SMN2 and TDRD3. SMN1/SMN2 interacts preferentially with the symmetrically dimethylated form while TDRD3 interacts with the asymmetric form. Through the recruitment of SMN1/SMN2, symmetric dimethylation is required for resolving RNA-DNA hybrids created by RNA polymerase II, that form R-loop in transcription terminal regions, an important step in proper transcription termination. CTD dimethylation may also facilitate the expression of select RNAs. Among tandem heptapeptide repeats of the C-terminal domain (CTD) some do not match the Y-S-P-T-S-P-S consensus, the seventh serine residue 'Ser-7' being replaced by a lysine. 'Lys-7' in these non-consensus heptapeptide repeats can be alternatively acetylated, methylated and dimethylated. Methylation occurs in the earliest transcription stages and precedes or is concomitant to 'Ser-5' and 'Ser-7' phosphorylation.
Ubiquitinated by WWP2 leading to proteasomal degradation (By similarity). Following UV treatment, the elongating form of RNA polymerase II (RNA pol IIo) is ubiquitinated UV damage sites without leading to degradation: ubiquitination is facilitated by KIAA1530/UVSSA and promotes RNA pol IIo backtracking to allow access to the nucleotide excision repair machinery. -
Cellular localization
Nucleus. - Information by UniProt
-
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 5430 Human
- Omim: 180660 Human
- SwissProt: P24928 Human
- Unigene: 270017 Human
-
Alternative names
- DNA directed RNA polymerase II A antibody
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase II largest subunit RNA polymerase II 220 kd subunit antibody
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit A antibody
see all
Images
-
All lanes : Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252)
Lane 2 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with Immunising peptide at 1 µg/ml
Lane 3 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with Non modified peptide at 1 µg/ml
Lane 4 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS peptide (ab12795) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 5 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) withS. cerevisiae RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S1606 + S1613) peptide (ab12793) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 6 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) withHuman RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S5) peptide (ab18488) at 1 µg/ml
Lysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) (ab97051) at 1/10000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 217 kDa
Observed band size: 250 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 118 kDa (possible non-specific binding), 50 kDa (possible non-specific binding), 70 kDa (possible non-specific binding)
Exposure time: 8 minutesThe predicted molecular weight of RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) is 217 kDa (SwissProt), however we expect to observe a banding pattern around 250 kDa.
This blot was produced using a 3-8% Tris Acetate gel under the TA buffer system. The gel was run at 150V for 60 minutes before being transferred onto a Nitrocellulose membrane at 30V for 70 minutes. The membrane was then blocked for an hour using 5% Bovine Serum Albumin before being incubated with ab126537 overnight at 4°C. Antibody binding was detected using an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP, and visualised using ECL development solution.
-
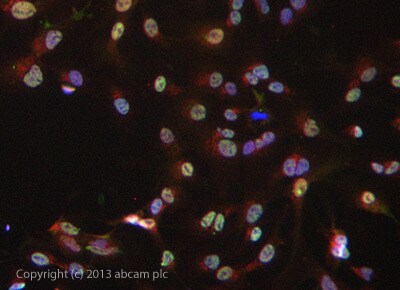 Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence - Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537)
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence - Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537)ab126537 stained HepG2 cells. The cells were 4% formaldehyde fixed (10 min) and then incubated in 1%BSA / 10% normal goat serum / 0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h to permeabilise the cells and block non-specific protein-protein interactions. The cells were then incubated with the antibody ab126537 at 5µg/ml overnight at +4°C. The secondary antibody (green) was DyLight® 488 goat anti- rabbit (ab96899) IgG (H+L) used at a 1/250 dilution for 1h. Alexa Fluor® 594 WGA was used to label plasma membranes (red) at a 1/200 dilution for 1h. DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue) at a concentration of 1.43µM.
-
ab126537 was tested using an Indirect ELISA approach. The wells were coated with peptide (1µg/ml at 100µl/well) overnight at 4°C, followed by a 5% BSA blocking step for 1 hour at room temperature. The primary Ab was then added at a dilution range of 1- 0.00025µg/ml (100µl/well) for 1hr at room temperature. A HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (heavy and light chain) was used as a secondary antibody at 1:20,000 dilution for 1hr at room temperature.
Protocols
Datasheets and documents
References (3)
ab126537 has been referenced in 3 publications.
- Sava GP et al. ABC-transporter upregulation mediates resistance to the CDK7 inhibitors THZ1 and ICEC0942. Oncogene 39:651-663 (2020). PubMed: 31530935
- Chakraborty P et al. DHX9 helicase promotes R-loop formation in cells with impaired RNA splicing. Nat Commun 9:4346 (2018). PubMed: 30341290
- He G et al. Cdk7 Is Required for Activity-Dependent Neuronal Gene Expression, Long-Lasting Synaptic Plasticity and Long-Term Memory. Front Mol Neurosci 10:365 (2017). PubMed: 29163040
Images
-
All lanes : Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252)
Lane 2 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with Immunising peptide at 1 µg/ml
Lane 3 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with Non modified peptide at 1 µg/ml
Lane 4 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) with S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS peptide (ab12795) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 5 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) withS. cerevisiae RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S1606 + S1613) peptide (ab12793) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 6 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate (ab27252) withHuman RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S5) peptide (ab18488) at 1 µg/ml
Lysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) (ab97051) at 1/10000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 217 kDa
Observed band size: 250 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 118 kDa (possible non-specific binding), 50 kDa (possible non-specific binding), 70 kDa (possible non-specific binding)
Exposure time: 8 minutesThe predicted molecular weight of RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) is 217 kDa (SwissProt), however we expect to observe a banding pattern around 250 kDa.
This blot was produced using a 3-8% Tris Acetate gel under the TA buffer system. The gel was run at 150V for 60 minutes before being transferred onto a Nitrocellulose membrane at 30V for 70 minutes. The membrane was then blocked for an hour using 5% Bovine Serum Albumin before being incubated with ab126537 overnight at 4°C. Antibody binding was detected using an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP, and visualised using ECL development solution.
-
 Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence - Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537)
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence - Anti-RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) antibody (ab126537)ab126537 stained HepG2 cells. The cells were 4% formaldehyde fixed (10 min) and then incubated in 1%BSA / 10% normal goat serum / 0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h to permeabilise the cells and block non-specific protein-protein interactions. The cells were then incubated with the antibody ab126537 at 5µg/ml overnight at +4°C. The secondary antibody (green) was DyLight® 488 goat anti- rabbit (ab96899) IgG (H+L) used at a 1/250 dilution for 1h. Alexa Fluor® 594 WGA was used to label plasma membranes (red) at a 1/200 dilution for 1h. DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue) at a concentration of 1.43µM.
-
ab126537 was tested using an Indirect ELISA approach. The wells were coated with peptide (1µg/ml at 100µl/well) overnight at 4°C, followed by a 5% BSA blocking step for 1 hour at room temperature. The primary Ab was then added at a dilution range of 1- 0.00025µg/ml (100µl/well) for 1hr at room temperature. A HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (heavy and light chain) was used as a secondary antibody at 1:20,000 dilution for 1hr at room temperature.













