Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)
Key features and details
- Rabbit polyclonal to Noggin
- Suitable for: IHC-P, WB
- Reacts with: Mouse, Human
- Isotype: IgG
Overview
-
Product name
Anti-Noggin antibody
See all Noggin primary antibodies -
Description
Rabbit polyclonal to Noggin -
Host species
Rabbit -
Tested applications
Suitable for: IHC-P, WBmore details
Unsuitable for: IHC-Fr -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mouse, Human
Predicted to work with: Horse, Chicken, Xenopus laevis
-
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide corresponding to Human Noggin aa 1-100 (internal sequence) conjugated to keyhole limpet haemocyanin.
(Peptide available asab16380) -
Positive control
- Purchase matching WB positive control:Recombinant human Noggin protein
- This antibody gave a positive signal in both Human and Mouse Noggin Recombinant protein.
Properties
-
Form
Liquid -
Storage instructions
Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Upon delivery aliquot. Store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. -
Storage buffer
pH: 7.40
Preservative: 0.02% Sodium azide
Constituent: PBS
Batches of this product that have a concentration Concentration information loading...
Concentration information loading...Purity
Immunogen affinity purifiedClonality
PolyclonalIsotype
IgGResearch areas
Associated products
-
Compatible Secondaries
-
Isotype control
-
Positive Controls
-
Recombinant Protein
Applications
Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab16054 in the following tested applications.
The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
Application Abreviews Notes IHC-P 1/175. Perform heat mediated antigen retrieval via the pressure cooker method before commencing with IHC staining protocol. WB Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 26, 35 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 26 kDa). Application notesIs unsuitable for IHC-Fr.Target
-
Function
Essential for cartilage morphogenesis and joint formation. Inhibitor of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP) signaling which is required for growth and patterning of the neural tube and somite. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in NOG are a cause of symphalangism proximal syndrome (SYM1) [MIM:185800]. SYM1 is characterized by the hereditary absence of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints (Cushing symphalangism). Severity of PIP joint involvement diminishes towards the radial side. Distal interphalangeal joints are less frequently involved and metacarpophalangeal joints are rarely affected whereas carpal bone malformation and fusion are common. In the lower extremities, tarsal bone coalition is common. Conducive hearing loss is seen and is due to fusion of the stapes to the petrous part of the temporal bone.
Defects in NOG are the cause of multiple synostoses syndrome type 1 (SYNS1) [MIM:186500]; also known as synostoses, multiple, with brachydactyly/symphalangism-brachydactyly syndrome. SYNS1 is characterized by tubular-shaped (hemicylindrical) nose with lack of alar flare, otosclerotic deafness, and multiple progressive joint fusions commencing in the hand. The joint fusions are progressive, commencing in the fifth proximal interphalangeal joint in early childhood (or at birth in some individuals) and progressing in an ulnar-to-radial and proximal-to-distal direction. With increasing age, ankylosis of other joints, including the cervical vertebrae, hips, and humeroradial joints, develop.
Defects in NOG are the cause of tarsal-carpal coalition syndrome (TCC) [MIM:186570]. TCC is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by fusion of the carpals, tarsals and phalanges, short first metacarpals causing brachydactyly, and humeroradial fusion. TCC is allelic to SYM1, and different mutations in NOG can result in either TCC or SYM1 in different families.
Defects in NOG are a cause of stapes ankylosis with broad thumb and toes (SABTS) [MIM:184460]; also known as Teunissen-Cremers syndrome. SABTS is a congenital autosomal dominant disorder that includes hyperopia, a hemicylindrical nose, broad thumbs, great toes, and other minor skeletal anomalies but lacked carpal and tarsal fusion and symphalangism.
Defects in NOG are the cause of brachydactyly type B2 (BDB2) [MIM:611377]. BDB2 is a subtype of brachydactyly characterized by hypoplasia/aplasia of distal phalanges in combination with distal symphalangism, fusion of carpal/tarsal bones, and partial cutaneous syndactyly. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the noggin family. -
Cellular localization
Secreted. - Information by UniProt
-
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 9241 Human
- Entrez Gene: 18121 Mouse
- Entrez Gene: 373646 Xenopus laevis
- Omim: 602991 Human
- SwissProt: Q13253 Human
- SwissProt: P97466 Mouse
- SwissProt: P49011 Xenopus laevis
- Unigene: 248201 Human
see all -
Alternative names
- Nog antibody
- NOGG_HUMAN antibody
- Noggin antibody
see all
Images
-
All lanes : Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Noggin Human Recombinant Protein
Lane 2 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein
Lysates/proteins at 0.1 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat polyclonal to Rabbit IgG - H&L - Pre-Adsorbed (HRP) at 1/3000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 26 kDa
Observed band size: 26,35 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Exposure time: 1 minute -
All lanes : Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein
Lane 2 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein with Human Noggin peptide (ab16380) at 1 µg/ml
Lysates/proteins at 0.01 µg per lane.
Predicted band size: 26 kDa -
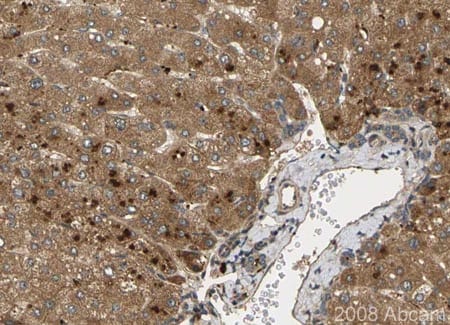 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)ab16054 stainning Noggin in paraffin-embedded human liver tissue, showing a cytoplasmic and/or membranous distribution in both hepatocytes and bile duct cells. Paraffin embedded tissue was incubated with ab16054 (1/175 dilution) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Antigen retrieval was performed by heat induction in citrate buffer pH 6. ab16054 was tested in a tissue microarray (TMA) containing a wide range of normal and cancer tissues as well as a cell microarray consisting of a range of commonly used, well characterised human cell lines.
-
 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.Immunohistochemical analysis of human small intestine tissue, labeling Noggin with ab16054. Tissue was formaldehyde fixed, treated with EDTA (pH 8.6) at 100°C for 20 minutes for heat-mediated antigen retrieval and blocked with 3% Hydrogen Peroxide for 10 minutes at 25°C. Incubation with ab16054 (diluted 1/400) was performed for 20 minutes at 25°C.
-
 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.Immunohistochemical analysis of mouse kidney tissue, labeling Noggin with ab16054. Tissue was paraformaldehyde fixed, treated with Citrate buffer for heat-mediated antigen retrieval and blocked with Serum Free Protein Block for 20 minutes. Incubation with ab16054 (diluted 1/2500) was performed for 15 hours at 4°C
Protocols
References (18)
ab16054 has been referenced in 18 publications.
- Harnisch K et al. Myelination in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Is Associated with Regulation of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 and Its Antagonist Noggin. Int J Mol Sci 20:N/A (2019). PubMed: 30609838
- Jiang Y et al. Identification of miR-200c-3p as a major regulator of SaoS2 cells activation induced by fluoride. Chemosphere 199:694-701 (2018). WB . PubMed: 29471239
- Shin HC et al. Modulation of hippocampal neuronal activity by So-ochim-tang-gamibang in mice subjected to chronic restraint stress. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:456 (2017). PubMed: 28888226
- Sharma S et al. Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine (SPARC) Mediates Metastatic Dormancy of Prostate Cancer in Bone. J Biol Chem 291:19351-63 (2016). PubMed: 27422817
- Goldie SJ et al. Mice lacking the conserved transcription factor Grainyhead-like 3 (Grhl3) display increased apposition of the frontal and parietal bones during embryonic development. BMC Dev Biol 16:37 (2016). IHC ; Mouse . PubMed: 27756203
Images
-
All lanes : Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Noggin Human Recombinant Protein
Lane 2 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein
Lysates/proteins at 0.1 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat polyclonal to Rabbit IgG - H&L - Pre-Adsorbed (HRP) at 1/3000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 26 kDa
Observed band size: 26,35 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Exposure time: 1 minute
-
All lanes : Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein
Lane 2 : Noggin Mouse Recombinant Protein with Human Noggin peptide (ab16380) at 1 µg/ml
Lysates/proteins at 0.01 µg per lane.
Predicted band size: 26 kDa
-
 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054)ab16054 stainning Noggin in paraffin-embedded human liver tissue, showing a cytoplasmic and/or membranous distribution in both hepatocytes and bile duct cells. Paraffin embedded tissue was incubated with ab16054 (1/175 dilution) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Antigen retrieval was performed by heat induction in citrate buffer pH 6. ab16054 was tested in a tissue microarray (TMA) containing a wide range of normal and cancer tissues as well as a cell microarray consisting of a range of commonly used, well characterised human cell lines.
-
 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.Immunohistochemical analysis of human small intestine tissue, labeling Noggin with ab16054. Tissue was formaldehyde fixed, treated with EDTA (pH 8.6) at 100°C for 20 minutes for heat-mediated antigen retrieval and blocked with 3% Hydrogen Peroxide for 10 minutes at 25°C. Incubation with ab16054 (diluted 1/400) was performed for 20 minutes at 25°C.
-
 Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.
Immunohistochemistry (Formalin/PFA-fixed paraffin-embedded sections) - Anti-Noggin antibody (ab16054) This image is courtesy of an anonymous Abreview.Immunohistochemical analysis of mouse kidney tissue, labeling Noggin with ab16054. Tissue was paraformaldehyde fixed, treated with Citrate buffer for heat-mediated antigen retrieval and blocked with Serum Free Protein Block for 20 minutes. Incubation with ab16054 (diluted 1/2500) was performed for 15 hours at 4°C


















