Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit (ab139418)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Cell-based
- Detection method: Fluorescent
- Sample type: Adherent cells, Suspension cells
Overview
-
Product name
Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit -
Detection method
Fluorescent -
Sample type
Adherent cells, Suspension cells -
Assay type
Cell-based -
Product overview
ab139418 is designed for quantitative DNA content analysis in tissue culture cells using the nucleic acid stain propidium iodide followed by flow cytometry analysis. Propidium iodide staining of DNA is the classic means of cell cycle analysis. The staining procedure takes less than 1 hour of total processing time and cells fixed in ethanol are stable for at least several weeks at 4ºC. The contents of this kit are sufficient for 200 assays.
Propidium iodide is a fluorescent molecule that binds nucleic acid with little or no sequence preference. Because Propidium iodide binds RNA as well as DNA, RNaseA (ribonuclease A) is included in this kit to digest cellular RNA and thus decrease background RNA staining from the experiment. Since Propidium iodide is membrane impermeant, ethanol is used to both fix and permeabilize cells. This kit is compatible with cells of any species that can be prepared as a single cell suspension. A flow cytometer is required for quantitative analysis.
-
Notes
Cell cycle analysis by quantitation of DNA content was one of the earliest applications of flow cytometry. The DNA of mammalian, yeast, plant or bacterial cells can be stained by a variety of DNA binding dyes. The premise with these dyes is that they are stoichiometric i.e. they bind in proportion to the amount of DNA present in the cell. In this way cells that are in S phase will have more DNA than cells in G1. They will take up proportionally more dye and will fluoresce more brightly until they have doubled their DNA content. The cells in G2 will be approximately twice as bright as cells in G1.
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 200 tests 10X Phosphate Buffered Saline 1 x 100ml 200X RNaseA 1 x 200µl 20X Propidium Iodide 1 x 2ml
Images
-
 Functional Studies - Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit (ab139418) Krishnan, Poorani et al., Scientific reports?vol. 7,1 10962., Fig 13, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-09140-1The cell cycle arrest caused by CPT-CEF in a concentration-dependent manner in A549 cells. (a) Untreated, (b) 1/2 IC50 treated cells and (c) IC50 treated A549 cells. (d) The graphical representation of the trend in cell cycle arrest of A549 cells in response to CPT-CEF treatment.
Functional Studies - Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit (ab139418) Krishnan, Poorani et al., Scientific reports?vol. 7,1 10962., Fig 13, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-09140-1The cell cycle arrest caused by CPT-CEF in a concentration-dependent manner in A549 cells. (a) Untreated, (b) 1/2 IC50 treated cells and (c) IC50 treated A549 cells. (d) The graphical representation of the trend in cell cycle arrest of A549 cells in response to CPT-CEF treatment. -
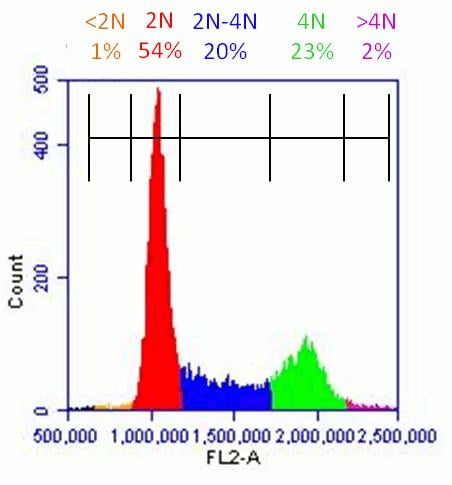
Sample analysis of an experiment using ab139418 on HeLa cells. Use flow cytometer software to establish markers on a histogram plot to quantify the percentage of cells with 4N DNA content.
-
Sample flow cytometry data using ab139418 on untreated HeLa cells. (A) Propidium iodide histogram with DNA content color coded. This is a typical result for untreated healthy cells: most cells are G1 stage (2N), some cells are undergoing DNA synthesis (2N-4N) and the final population is mitotic (4N). Very few cells are apoptotic (4N). (B) Ungated Forward and Side-scatter plot for HeLa cells in which has been pseudo-colored based on the DNA content shown in (A). Note that cell size is proportional to DNA content. (C) Gated Forward and Side-scatter plot which excludes the small debris (lower left) and cell aggregates (upper right) that are seen in (B). This is the gate used for the Propidium Iodide histogram shown in (A).
-
Comparison of fixation and staining conditions using ab139418 on Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were untreated (Control) or treated with Thymidine or Nocodazole for 24h. Parallel plates of cells were fixed with 66% Ethanol, 66% Methanol or 4% Paraformaldehyde; each preparation was then stained with propidium iodine with or without the addition of RNase. For each fixation condition, treatment with RNase yields tighter propidium iodide peaks. Moreover, Ethanol and Methanol fixation yield superior Propidium iodide data relative to Paraformaldehyde fixation.
-
Sample experiment using ab139418 on HeLa cells treated with Thymidine and Nocodazole. (A) Untreated HeLa cells with the expected distribution of cells with 2N, 2N-4N and 4N DNA content. (B) HeLa cells treated with Thymidine have predominantly 2N DNA content. Thymidine inhibits DNA synthesis. (C) HeLa cells treated with Nocodazole have predominantly 4N DNA content. Nocodazole is a microtubule inhibitor that causes mitotic arrest.