NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab65348)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 2 hr
- Sample type: Cell Lysate, Serum, Tissue Lysate, Urine
Overview
-
Product name
NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
See all NAD/NADH kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Urine, Serum, Cell Lysate, Tissue Lysate -
Assay type
Quantitative -
Range
20 nM - 2000 nM -
Assay time
2h 00m -
Product overview
NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) ab65348 provides a convenient and sensitive tool to quantify NAD+ and NADH, and measure their ratio, in samples from mammals and other species.
The NAD cycling enzyme mix in the kit specifically acts on NADH/NAD in an enzyme cycling reaction which significantly increases sensitivity and specificity. There is no requirement to purify NADH/NAD from samples.
The levels of both NADt (total NAD+ and NADH) and NADH can be easily measured; the level of NAD+ can be easily calculated by subtracting NADH from NADt. The assay is read by absorbance at 450 nm.
NAD / NADH assay protocol summary:
- extract samples from cells / tissues with extraction buffer and deproteinize with spin column
- for NADH measurement, heat samples to 60ºC for 30 min to decompose NAD+, cool on ice (this step not necessary for measurement of total NAD+/NADH)
- add samples and standards to wells
- add reaction mix and incubate for 5 min at room temp to convert NAD to NADH
- add NADH developer and incubate for 1-4 hrs while reaction cycles
- analyze with microplate reader multiple times during the 1-4 hr incubation
- reaction can be stopped with stop solutionChinese protocol available. See protocols section below.
-
Notes
This assay specifically detects NAD and NADH, but not NADP nor NADPH.
If you would like to use a fluorometric reading, please refer to NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab176723).
NAD/NADH Assay kit ab221821 uses an alternative assay method that relies on purification of NAD and NADH from samples and may be more sensitive in some samples.
Review our Metabolism Assay Guide to learn about assays for metabolites, metabolic enzymes, mitochondrial function, and oxidative stress, and also about how to assay metabolic function in live cells using your plate reader.
How other researchers have used NAD/NADH Assay Kit ab65348
This NAD/NADH assay kit has been used in publications in a variety of sample types, including:
- Human: primary blood mononuclear cells1, epithelial ovarian cancer cells2, Jurkat cells3
- Mouse: cell culture lysates4, cardiomyocyte cell culture lysates5, liver6, liver and muscle7, primary hepatocyte cell cultures8, aorta tissue9
- Rat: brain tissue10
- Locust: thoraic muscle11
Bacteria: Z mobilis12, E coli13References: 1 - Castro-Marrero J et al 2015; 2 - Zhu J et al 2019, Xia H et al 2015; 3 - Miller TW et al 2015; 4 - Mekala NK et al 2019, Ling S et al 2017; 5 - Zhang D et al 2019; 6 - Shao D et al 2017, Mukherji A et al 2015, Yu JH et al 2016; 7 - Karandrea S et al 2017; 8 - Traboulsi H et al 2014; 9 - Liu Y et al 2016; 10 - Rao G et al 2016; 11 - Ding D et al 2018; 12 - Wu B et al 2019; 13 - Long YM et al 2017
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components Identifier 100 tests NAD Cycling Buffer NM 1 x 15ml NAD Cycling Enzyme Mix Green 1 vial NADH Developer Purple 1 vial NADH Standard (MW:663.4) Yellow 1 vial NADH/NAD Extraction Buffer NM 1 x 50ml Stop Solution Red 1 x 1.2ml -
Research areas
-
Relevance
NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme in metabolic redox reactions, a precursor for several cell signaling molecules, and a substrate for protein posttranslational modifications. NAD is a dinucleotide, consisting of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide. In metabolism, NAD is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is therefore found in two forms in cells: NAD is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced, forming NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins in posttranslational modifications.
Images
-
 Functional Studies - NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab65348) Karandrea, Shpetim et al., PloS one vol. 12,9 e0185374., Fig 6, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185374
Functional Studies - NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab65348) Karandrea, Shpetim et al., PloS one vol. 12,9 e0185374., Fig 6, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185374NADH/NAD+ ratio in soleus muscle measured useing ab65348. p ? 0.05 when comparing (+) HFD and LFD, (*) HFD + TQ and HFD, and (#) LFD and LFD + TQ using independent t-tests. Results are means ± SEM (n = 8-10 mice per treatment group). LFD: low fat diet, HFD: high fat diet, TQ: thymoquinone.
-
 Functional Studies - NAD/NADH Assay Kit (ab65348) Ren JG et al., PLoS One, 5, , 2010 Reproduced under the Creative Commons license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NAD/NADH was measured in K562 ME2 knockdown cells(pLKO - empty vector; shME2-2 & shME2-3 - two selected knockdown clones). Data are expressed as mean ±: SD, n=3. NAD/NADH Ratio is calculated as described in the product protocol. Image obtained from Ren JG et al; PLOS one, 2010; 5(9): e12520 (DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0012520)
Functional Studies - NAD/NADH Assay Kit (ab65348) Ren JG et al., PLoS One, 5, , 2010 Reproduced under the Creative Commons license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/NAD/NADH was measured in K562 ME2 knockdown cells(pLKO - empty vector; shME2-2 & shME2-3 - two selected knockdown clones). Data are expressed as mean ±: SD, n=3. NAD/NADH Ratio is calculated as described in the product protocol. Image obtained from Ren JG et al; PLOS one, 2010; 5(9): e12520 (DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0012520) -
NAD and NADH (tNAD) or NADH alone measured cell lysates. 5e6 cells were lysed in 1 mL, spin filtered, and tested neat or 1/5 (duplicates +/- SD).
-
Standard curve with background signal subtracted (duplicates; +/- SD).
-
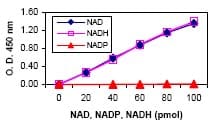
NADH Standard calibration curve. Quantification of NAD (diamond) and NADH (open square) following product protocol and using NADH standard provided in the kit. No NADP (triangle) was detected in this reaction.