MAPK (ATF2, c-Jun, c-Myc, MEF2, STAT1alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab207212)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Semi-quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Assay time: 3 hr 30 min
- Sample type: Nuclear Extracts
- Sensitivity: 500 ng/well
Overview
-
Product name
MAPK (ATF2, c-Jun, c-Myc, MEF2, STAT1alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Nuclear Extracts -
Assay type
Semi-quantitative -
Sensitivity
500 ng/well -
Assay time
3h 30m -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mouse, Human -
Product overview
MAPK (ATF2, c-Jun, c-Myc, MEF2, STAT1alpha) Transcription Factor Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab207212) is a high throughput assay to quantify activation of MAPK regulated transcription factors. This assay combines a quick ELISA format with a sensitive and specific non-radioactive assay for transcription factor activation.
A specific double stranded DNA sequence containing the MAPK consensus binding site has been immobilized onto a 96-well plate. Active MAPK present in the nuclear extract specifically binds to the oligonucleotide. MAPK is detected by a primary antibody that recognizes an epitope of MAPK accessible only when the protein is activated and bound to its target DNA. An HRP-conjugated secondary antibody provides sensitive colorimetric readout at OD 450 nm. This product detects human MAPK and mice c-Myc, c Jund and Jun D.
Key performance and benefits:
- Assay time: 3.5 hours (cell extracts preparation not included).
- Detection limit:
- Detection range: 0.5 – 5 µg of nuclear extract/well for c-Myc, MEF2 and STAT1; 1 – 10 µg nuclear extract/well for ATF-2 and c-Jun.
-
Notes
The transmission of extracellular signals into intracellular responses is a complex process that often involves the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). The MAPK pathway is a three kinase cascade consisting of a MAPK kinase (MAPKKK or MEKK) that activates a MAP/ERK kinase (MEK or MAPKK). This stimulates a phosphorylation-dependent increase in the activity of the MAP kinase. Upon activation, MAPKs phosphorylate a variety of intracellular targets including transcription factors, transcription adaptor proteins, membrane and cytoplasmic substrates as well as other protein kinases.
At least three parallel MAPK pathways exist in humans. The extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathway primarily transmits mitogenic and differentiation stimuli, while the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 pathways predominantly transmit stress and cytokine stimuli. c-Myc, an ERK substrate, is a transcription factor that regulates cell growth and differentiation, glycolysis and apoptosis. Deregulation of c-Myc has been implicated in the origin of diverse human cancers. Elk-1 is a member of the ternary complex factor (TCF) sub-family of the ETS domain family. Elk-1 can be stimulated by all three MAPK pathways, and its main function is the regulation of the activity of the c-Fos promoter in response to extracellular stimuli. MEF2, a member of the MADS box family, is mainly involved in muscle differentiation, but also plays roles in muscle hypertrophy, neuronal survival and T-cell apoptosis. MEF2 is activated by both the p38 and ERK5 pathways.1 STAT1 is involved in activation of IFNα and γ genes, and is activated by p38 and JNK pathways. c-Jun is a member of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) family and is activated by both ERK1/2 and JNK pathways.2 AP-1 members play roles in the expression of genes involved in proliferation and cell cycle progression. ATF-2 is a member of the ATF/CREB family that binds to the cAMP response element (CRE). ATF-2 is activated by ERK1/2, JNK and p38.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 2 x 96 tests 10X Antibody Binding Buffer 2 x 2.2ml 10X Wash Buffer 1 x 60ml 96-well MAPK assay plate 2 units Anti-mouse HRP-conjugated IgG 1 x 11µl Anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated IgG (0.25 μg/μL) 2 x 11µl AP-1 Mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl AP-1 Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl ATF-2 Mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/µL) 1 x 100µl ATF-2 Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/µL) 1 x 100µl Binding Buffer 1 x 10ml c-Myc antibody 1 x 11µl c-Myc Mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl c-Myc Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl Developing Solution 2 x 11ml Dithiothreitol (DTT) (1 M) 1 x 100µl K-562(TPA) nuclear extract (2.5µg/μL) 1 x 40µl Lysis Buffer 1 x 10ml MEF2 antibody 1 x 11µl MEF2 mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl MEF2 wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl Phospho-c-Jun antibody 1 x 22µl Phosphorylated ATF-2 antibody 1 x 11µl Plate sealer 2 units Protease Inhibitor Cocktail 1 x 100µl STAT mutated oligonucleotide (10 pmol/μL) 1 x 100µl STAT Wild-type oligonucleotide (10 pmol/µL) 1 x 100µl STAT1α antibody 1 x 11µl Stop Solution 1 x 60ml -
Research areas
-
Relevance
MAPK is activated by phosphorylation, whereupon the protein translocates to the nucleus, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. MAPK is an important integration point of many signalling pathways, for a range of cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. -
Alternative names
- ERK1
- ERT2
- Extracellular signal regulated kinase 1
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 5595 Human
- Entrez Gene: 26417 Mouse
- Omim: 601795 Human
- SwissProt: P27361 Human
- SwissProt: Q63844 Mouse
- Unigene: 861 Human
- Unigene: 8385 Mouse
Images
-
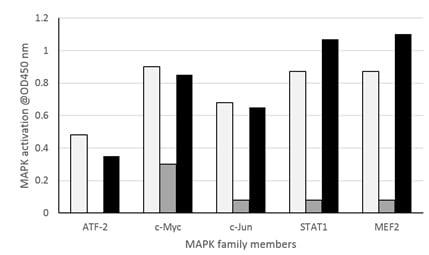
Nuclear extracts from various cell lines were tested for ATF2, c-Myc, c-Jun, STAT1 and MEF2 activation. Cell lines used were HeLa (anisomycin-treated) for ATF2, Jurkat (1 day growth) for c-Myc, K-562 (TPA-treated) for c- Jun, U-937 (TPA + IFNγ treated) for STAT1 and C2C12 for MEF2. Activation was also monitored in the absence (grey) and in the presence of wild-type (black) or mutated (white) consensus binding oligonucleotides. Note that the wild-type oligonucleotide reduces binding of the transcription factors by over 90%, while incubation with the mutant MAPK competitor oligos have limited effect on DNA binding. These results are provided for demonstration purposes only.