Human GFAP ELISA Kit (ab223867)
Key features and details
- One-wash 90 minute protocol
- Sensitivity: 47 pg/ml
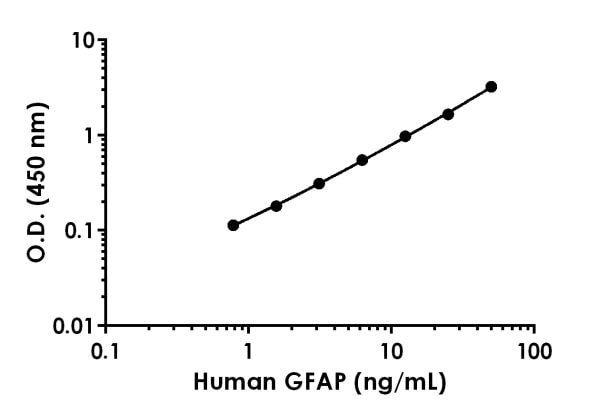
- Range: 0.781 ng/ml - 50 ng/ml
- Sample type: Tissue Extracts
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Assay type: Sandwich (quantitative)
- Reacts with: Human
Overview
-
Product name
Human GFAP ELISA Kit
See all GFAP kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Precision
Intra-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Brain 8 5.3% Inter-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Brain 3 11.8% -
Sample type
Tissue Extracts -
Assay type
Sandwich (quantitative) -
Sensitivity
47 pg/ml -
Range
0.781 ng/ml - 50 ng/ml -
Recovery
Sample specific recovery Sample type Average % Range Tissue Extracts 117 116% - 119% -
Assay time
1h 30m -
Assay duration
One step assay -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human -
Product overview
Human GFAP ELISA Kit (ab223867) is a single-wash 90 min sandwich ELISA designed for the quantitative measurement of GFAP protein in tissue extracts. It uses our proprietary SimpleStep ELISA® technology. Quantitate Human GFAP with 47 pg/ml sensitivity.
SimpleStep ELISA® technology employs capture antibodies conjugated to an affinity tag that is recognized by the monoclonal antibody used to coat our SimpleStep ELISA® plates. This approach to sandwich ELISA allows the formation of the antibody-analyte sandwich complex in a single step, significantly reducing assay time. See the SimpleStep ELISA® protocol summary in the image section for further details. Our SimpleStep ELISA® technology provides several benefits:
- Single-wash protocol reduces assay time to 90 minutes or less
- High sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility from superior antibodies
- Fully validated in biological samples
- 96-wells plate breakable into 12 x 8 wells stripsA 384-well SimpleStep ELISA® microplate (ab203359) is available to use as an alternative to the 96-well microplate provided with SimpleStep ELISA® kits.
-
Notes
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a class-III intermediate filament, cell-specific marker that during development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells. Protein expression is also found in numerous cell types including astrocytes, ependymal cells, osteocytes, keratinocytes and chondrocytes. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in rat glomeruli, peritubular fibroblasts, stellate cells of the pancreas and liver tissue as well as Leydig cells of the testis in both hamsters and humans.
Abcam has not and does not intend to apply for the REACH Authorisation of customers’ uses of products that contain European Authorisation list (Annex XIV) substances.
It is the responsibility of our customers to check the necessity of application of REACH Authorisation, and any other relevant authorisations, for their intended uses. -
Platform
Pre-coated microplate (12 x 8 well strips)
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at +4°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 1 x 96 tests 10X Wash Buffer PT (ab206977) 1 x 20ml 50X Cell Extraction Enhancer Solution (ab193971) 1 x 1ml 5X Cell Extraction Buffer PTR (ab193970) 1 x 10ml Antibody Diluent CP 1 x 6ml 10X Human GFAP Capture Antibody 1 x 600µl 10X Human GFAP Detector Antibody 1 x 600µl Human GFAP Lyophilized Recombinant Protein 2 vials Plate Seals 1 unit Sample Diluent NS (ab193972) 1 x 12ml SimpleStep Pre-Coated 96-Well Microplate (ab206978) 1 unit Stop Solution 1 x 12ml TMB Development Solution 1 x 12ml -
Research areas
-
Function
GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-specific marker that, during the development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells. -
Tissue specificity
Expressed in cells lacking fibronectin. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in GFAP are a cause of Alexander disease (ALEXD) [MIM:203450]. Alexander disease is a rare disorder of the central nervous system. It is a progressive leukoencephalopathy whose hallmark is the widespread accumulation of Rosenthal fibers which are cytoplasmic inclusions in astrocytes. The most common form affects infants and young children, and is characterized by progressive failure of central myelination, usually leading to death usually within the first decade. Infants with Alexander disease develop a leukoencephalopathy with macrocephaly, seizures, and psychomotor retardation. Patients with juvenile or adult forms typically experience ataxia, bulbar signs and spasticity, and a more slowly progressive course. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the intermediate filament family. -
Post-translational
modificationsPhosphorylated by PKN1. -
Cellular localization
Cytoplasm. Associated with intermediate filaments. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- wu:fb34h11
- ALXDRD
- cb345
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 2670 Human
- Omim: 137780 Human
- SwissProt: P14136 Human
- Unigene: 514227 Human
Images
-
SimpleStep ELISA technology allows the formation of the antibody-antigen complex in one single step, reducing assay time to 90 minutes. Add samples or standards and antibody mix to wells all at once, incubate, wash, and add your final substrate. See protocol for a detailed step-by-step guide.
-
Background-subtracted data values (mean +/- SD) are graphed.
-
 Interpolated concentrations of native GFAP in Human brain extract based on a 100 ng/mL extract load.
Interpolated concentrations of native GFAP in Human brain extract based on a 100 ng/mL extract load.The concentrations of GFAP were measured in duplicate and interpolated from the GFAP standard curve and corrected for sample dilution. The interpolated dilution factor corrected values are plotted (mean +/- SD, n=2). The mean GFAP concentration was determined to be 46.27 ng/mL per 100 ng/ml extract load.
-
To learn more about the advantages of recombinant antibodies see here.