HIF-1 alpha Transcription Factor Assay Kit (ab133104)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Semi-quantitative
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Sample type: Cell culture extracts, Cell Lysate
Overview
-
Product name
HIF-1 alpha Transcription Factor Assay Kit
See all HIF-1 alpha kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Cell culture extracts, Cell Lysate -
Assay type
Semi-quantitative -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mouse, Rat, Human
Predicted to work with: Mammals
-
Product overview
HIF-1 alpha Transcription Factor Assay (ab133104) is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting specific transcription factor DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts and whole cell lysate.
A 96-well enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) replaces the cumbersome radioactive electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). A specific double stranded DNA (dsDNA) sequence containing the HIF-1 alpha response element (5’-ACGTG-3’) is immobilized to the wells of a 96-well plate. HIF-1 alpha contained in a nuclear extract, binds specifically to the HIF-1 alpha response element. The HIF transcription factor complex is detected by addition of a specific primary antibody directed against HIF-1 alpha. A secondary antibody conjugated to HRP is added to provide a sensitive colorimetric readout at 450 nm.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Please refer to protocols. -
Components 96 tests 96-Well Plate Cover 1 unit Polysorbate 20 1 vial Transcription Factor Antibody Binding Buffer (10X) 1 x 3ml Transcription Factor Binding Assay Buffer (4X) 1 x 3ml Transcription Factor Developing Solution 1 x 12ml Transcription Factor Goat Anti-Rabbit HRP Conjugate 1 x 100µl Transcription Factor HIF-1 alpha 96-Well Strip Plate 1 unit Transcription Factor HIF-1 alpha Competitor dsDNA 1 vial Transcription Factor HIF-1 alpha Positive Control 1 vial Transcription Factor HIF-1 alpha Primary Antibody 1 vial Transcription Factor Reagent A 1 x 120µl Transcription Factor Stop Solution 1 x 12ml Wash Buffer Concentrate (400X) 1 x 5ml -
Research areas
-
Function
Functions as a master transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia. Under hypoxic conditions activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including, erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. Plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease. Binds to core DNA sequence 5'-[AG]CGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters. Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBPB and EP300. Activity is enhanced by interaction with both, NCOA1 or NCOA2. Interaction with redox regulatory protein APEX seems to activate CTAD and potentiates activation by NCOA1 and CREBBP. -
Tissue specificity
Expressed in most tissues with highest levels in kidney and heart. Overexpressed in the majority of common human cancers and their metastases, due to the presence of intratumoral hypoxia and as a result of mutations in genes encoding oncoproteins and tumor suppressors. -
Sequence similarities
Contains 1 basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain.
Contains 1 PAC (PAS-associated C-terminal) domain.
Contains 2 PAS (PER-ARNT-SIM) domains. -
Domain
Contains two independent C-terminal transactivation domains, NTAD and CTAD, which function synergistically. Their transcriptional activity is repressed by an intervening inhibitory domain (ID). -
Post-translational
modificationsIn normoxia, is hydroxylated on Pro-402 and Pro-564 in the oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD) by EGLN1/PHD1 and EGLN2/PHD2. EGLN3/PHD3 has also been shown to hydroxylate Pro-564. The hydroxylated prolines promote interaction with VHL, initiating rapid ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Deubiquitinated by USP20. Under hypoxia, proline hydroxylation is impaired and ubiquitination is attenuated, resulting in stabilization.
In normoxia, is hydroxylated on Asn-803 by HIF1AN, thus abrogating interaction with CREBBP and EP300 and preventing transcriptional activation. This hydroxylation is inhibited by the Cu/Zn-chelator, Clioquinol.
S-nitrosylation of Cys-800 may be responsible for increased recruitment of p300 coactivator necessary for transcriptional activity of HIF-1 complex.
Requires phosphorylation for DNA-binding.
Sumoylated; by SUMO1 under hypoxia. Sumoylation is enhanced through interaction with RWDD3. Desumoylation by SENP1 leads to increased HIF1A stability and transriptional activity.
Ubiquitinated; in normoxia, following hydroxylation and interaction with VHL. Lys-532 appears to be the principal site of ubiquitination. Clioquinol, the Cu/Zn-chelator, inhibits ubiquitination through preventing hydroxylation at Asn-803.
The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of asparagine is (S) stereospecific within HIF CTAD domains. -
Cellular localization
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic in normoxia, nuclear translocation in response to hypoxia. Colocalizes with SUMO1 in the nucleus, under hypoxia. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- ARNT interacting protein
- ARNT-interacting protein
- Basic helix loop helix PAS protein MOP1
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 3091 Human
- Entrez Gene: 15251 Mouse
- Entrez Gene: 29560 Rat
- Omim: 603348 Human
- SwissProt: Q16665 Human
- SwissProt: Q61221 Mouse
- SwissProt: O35800 Rat
- Unigene: 597216 Human
see all
Images
-
HEK293 cells were treated with 1 mM deferoxamine mesylate (DFO) for 1 or 24 hours. 40 micoliters of nuclear lysates (ab113474; corresponding to 4e6 cells) were tested in duplicates (+/- SD).
-
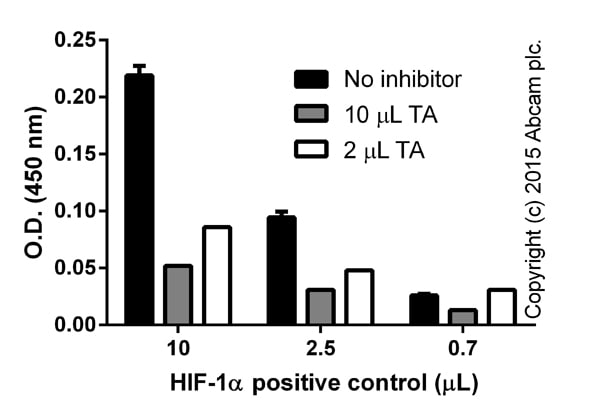
Titration of positive control with different volumes of inhibitor (TA), background signal subtracted (duplicates; +/- SD).
-
Titration of positive control, background signal subtracted (duplicates; +/- SD).
-
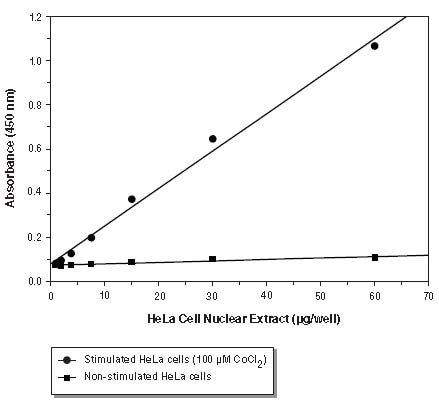
Assay of nuclear extract from stimulated HeLa cells (100 µM CoCl2) and non-stimulated HeLa cells.