Cholinesterase Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab235937)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Enzyme activity (quantitative)
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Sample type: Whole Blood
Overview
-
Product name
Cholinesterase Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
See all Butyrylcholinesterase kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Whole Blood -
Assay type
Enzyme activity (quantitative) -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mammals, Other species -
Product overview
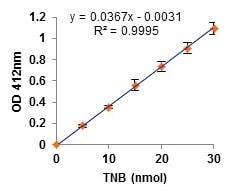
Cholinesterase Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab235937) combines the specific acetylcholinesterase (AChE; EC 3.1.1.7) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; EC 3.1.1.8) substrates and a selective BChE inhibitor to measure and distinguish AChE and BChE activities in Whole Blood samples without separating plasma from erythrocytes. The principle is based on the ability of AChE and BChE to hydrolyze their respective substrates and produce thiocholine. Thiocholine reacts with 5,5’-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) generating a yellow chromophore (TNB) that can be quantified at 412 nm. It is simple, easy to implement, and useful in clinical research to monitor exposure to anti- Cholinesterase compounds in blood Samples.
-
Notes
Cholinesterase (ChE) consists of a group of enzymes that hydrolyze choline esters. There are two ChE isoenzymes in blood: acetylcholinesterase (AChE; EC 3.1.1.7), also known as erythrocytes or true ChE, which is found mainly in red blood cells; and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; EC 3.1.1.8), also known as plasma ChE or pseudo-ChE, which is present in plasma. Blood AChE or BChE activity would be selectively reduced by exposing them to poisonous chemical agents, insecticides such as organophosphates or carbamates, anesthetics, and a variety of therapeutic drugs including donepezil or rivastigmine which are used for treating Alzheimer’s diseases. Therefore, Blood Cholinesterases (ChE=AChE+BChE) are potential biomarkers of suppressed and/or increased central and peripheral nervous system activity and tools for confirming possible therapeutics. Since plasma BChE and erythrocyte AChE can be selectively inhibited by certain insecticides or drugs, quantification of both isoenzymes’ activities is important.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 100 tests ChE Assay Buffer 1 x 100ml AChE Substrate 1 vial BChE Substrate (in DMSO) 1 x 100µl Acetylcholinesterase 1 vial Butyrylcholinesterase 1 vial BChE Inhibitor 1 vial DTNB 2 vials TNB Standard 1 vial -
Research areas
-
Function
Esterase with broad substrate specificity. Contributes to the inactivation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Can degrade neurotoxic organophosphate esters. -
Tissue specificity
Detected in blood plasma (at protein level). Present in most cells except erythrocytes. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in BCHE are the cause of butyrylcholinesterase deficiency (BChE deficiency) [MIM:177400]. BChE deficiency is a metabolic disorder characterized by prolonged apnoea after the use of certain anesthetic drugs, including the muscle relaxants succinylcholine or mivacurium and other ester local anesthetics. The duration of the prolonged apnoea varies significantly depending on the extent of the enzyme deficiency. BChE deficiency is a multifactorial disorder. The hereditary condition is transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family. -
Cellular localization
Secreted. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- Acylcholine acylhydrolase
- BCHE
- Butyrylcholine esterase
see all