Anti-ABCA4 antibody (ab72955)
Key features and details
- Rabbit polyclonal to ABCA4
- Suitable for: WB
- Reacts with: Mouse, Human
- Isotype: IgG
Overview
-
Product name
Anti-ABCA4 antibody
See all ABCA4 primary antibodies -
Description
Rabbit polyclonal to ABCA4 -
Host species
Rabbit -
Tested Applications & Species
See all applications and species dataApplication Species WB MouseRatHuman -
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide corresponding to Human ABCA4 aa 2250 to the C-terminus (C terminal) conjugated to keyhole limpet haemocyanin.
(Peptide available asab87350) -
Positive control
- This antibody gave a positive signal in Human and Mouse Retina Tissue lysates.
-
General notes
Reproducibility is key to advancing scientific discovery and accelerating scientists’ next breakthrough.
Abcam is leading the way with our range of recombinant antibodies, knockout-validated antibodies and knockout cell lines, all of which support improved reproducibility.
We are also planning to innovate the way in which we present recommended applications and species on our product datasheets, so that only applications & species that have been tested in our own labs, our suppliers or by selected trusted collaborators are covered by our Abpromise™ guarantee.
In preparation for this, we have started to update the applications & species that this product is Abpromise guaranteed for.
We are also updating the applications & species that this product has been “predicted to work with,” however this information is not covered by our Abpromise guarantee.
Applications & species from publications and Abreviews that have not been tested in our own labs or in those of our suppliers are not covered by the Abpromise guarantee.
Please check that this product meets your needs before purchasing. If you have any questions, special requirements or concerns, please send us an inquiry and/or contact our Support team ahead of purchase. Recommended alternatives for this product can be found below, as well as customer reviews and Q&As.
Properties
-
Form
Liquid -
Storage instructions
Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Upon delivery aliquot. Store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. -
Storage buffer
pH: 7.40
Preservative: 0.02% Sodium azide
Constituent: PBS
Batches of this product that have a concentration Concentration information loading...
Concentration information loading...Purity
Immunogen affinity purifiedClonality
PolyclonalIsotype
IgGResearch areas
Associated products
-
Compatible Secondaries
-
Isotype control
-
Recombinant Protein
Applications
The Abpromise guarantee
Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab72955 in the following tested applications.
The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
GuaranteedTested applications are guaranteed to work and covered by our Abpromise guarantee.
PredictedPredicted to work for this combination of applications and species but not guaranteed.
IncompatibleDoes not work for this combination of applications and species.
Application Species WB MouseRatHumanAll applications CowDogMacaque monkeyApplication Abreviews Notes WB Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 238 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 256 kDa).Notes WB
Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 238 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 256 kDa).Target
-
Function
In the visual cycle, acts as an inward-directed retinoid flipase, retinoid substrates imported by ABCA4 from the extracellular or intradiscal (rod) membrane surfaces to the cytoplasmic membrane surface are all-trans-retinaldehyde (ATR) and N-retinyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (NR-PE). Once transported to the cytoplasmic surface, ATR is reduced to vitamin A by trans-retinol dehydrogenase (tRDH) and then transferred to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) where it is converted to 11-cis-retinal. May play a role in photoresponse, removing ATR/NR-PE from the extracellular photoreceptor surfaces during bleach recovery. -
Tissue specificity
Retinal-specific. Seems to be exclusively found in the rims of rod photoreceptor cells. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in ABCA4 are the cause of Stargardt disease type 1 (STGD1) [MIM:248200]. STGD is one of the most frequent causes of macular degeneration in childhood. It is characterized by macular dystrophy with juvenile-onset, rapidly progressive course, alterations of the peripheral retina, and subretinal deposition of lipofuscin-like material. STGD1 inheritance is autosomal recessive.
Defects in ABCA4 are the cause of fundus flavimaculatus (FFM) [MIM:248200]. FFM is an autosomal recessive retinal disorder very similar to Stargardt disease. In contrast to Stargardt disease, FFM is characterized by later onset and slowly progressive course.
Defects in ABCA4 may be a cause of age-related macular degeneration type 2 (ARMD2) [MIM:153800]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid (known as drusen) that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin-containing structure known as Bruch membrane.
Defects in ABCA4 are the cause of cone-rod dystrophy type 3 (CORD3) [MIM:604116]. CORDs are inherited retinal dystrophies belonging to the group of pigmentary retinopathies. CORDs are characterized by retinal pigment deposits visible on fundus examination, predominantly in the macular region, and initial loss of cone photoreceptors followed by rod degeneration. This leads to decreased visual acuity and sensitivity in the central visual field, followed by loss of peripheral vision. Severe loss of vision occurs earlier than in retinitis pigmentosa.
Defects in ABCA4 are the cause of retinitis pigmentosa type 19 (RP19) [MIM:601718]. RP leads to degeneration of retinal photoreceptor cells. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. RP19 is characterized by choroidal atrophy. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the ABC transporter superfamily. ABCA family.
Contains 2 ABC transporter domains. -
Cellular localization
Membrane. Localized to outer segment disk edges of rods and cones, with around one million copies/photoreceptor. - Information by UniProt
-
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 24 Human
- Entrez Gene: 11304 Mouse
- Omim: 601691 Human
- SwissProt: P78363 Human
- SwissProt: O35600 Mouse
- Unigene: 416707 Human
- Unigene: 3918 Mouse
-
Alternative names
- ABC 10 antibody
- ABC A4 antibody
- ABC transporter, retinal-specific antibody
see all
Images
-
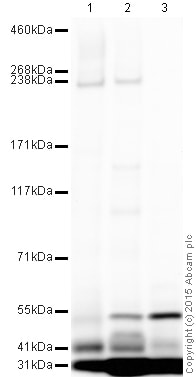
All lanes : Anti-ABCA4 antibody (ab72955) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Eye (Human) - adult normal Tissue Lysate
Lane 2 : Retina (Mouse) Tissue Lysate
Lane 3 : Retina (Rat) Tissue Lysate
Lysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) preadsorbed at 1/50000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 256 kDa
Observed band size: 235 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 31 kDa, 41 kDa, 55 kDa. We are unsure as to the identity of these extra bands.
Exposure time: 8 minutesThis blot was produced using a 3-8% Tris Acetate gel under the TA buffer system. The gel was run at 150V for 60 minutes before being transferred onto a Nitrocellulose membrane at 30V for 70 minutes. The membrane was then blocked for an hour using 2% Bovine Serum Albumin before being incubated with ab72955 overnight at 4°C. Antibody binding was detected using an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP, and visualised using ECL development solution ab133406.
Datasheets and documents
References (4)
ab72955 has been referenced in 4 publications.
- Wang M et al. Proteomic evidence that ABCA4 is vital for traumatic proliferative vitreoretinopathy formation and development. Exp Eye Res 181:232-239 (2019). PubMed: 30738069
- Lenis TL et al. Expression of ABCA4 in the retinal pigment epithelium and its implications for Stargardt macular degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E11120-E11127 (2018). PubMed: 30397118
- McClements ME et al. An AAV Dual Vector Strategy Ameliorates the Stargardt Phenotype in Adult Abca4-/- Mice. Hum Gene Ther N/A:N/A (2018). PubMed: 30381971
- McClements ME et al. A fragmented adeno-associated viral dual vector strategy for treatment of diseases caused by mutations in large genes leads to expression of hybrid transcripts. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther 7:N/A (2016). PubMed: 28239514
Images
-
All lanes : Anti-ABCA4 antibody (ab72955) at 1 µg/ml
Lane 1 : Eye (Human) - adult normal Tissue Lysate
Lane 2 : Retina (Mouse) Tissue Lysate
Lane 3 : Retina (Rat) Tissue Lysate
Lysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.
Secondary
All lanes : Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) preadsorbed at 1/50000 dilution
Developed using the ECL technique.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Predicted band size: 256 kDa
Observed band size: 235 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 31 kDa, 41 kDa, 55 kDa. We are unsure as to the identity of these extra bands.
Exposure time: 8 minutesThis blot was produced using a 3-8% Tris Acetate gel under the TA buffer system. The gel was run at 150V for 60 minutes before being transferred onto a Nitrocellulose membrane at 30V for 70 minutes. The membrane was then blocked for an hour using 2% Bovine Serum Albumin before being incubated with ab72955 overnight at 4°C. Antibody binding was detected using an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP, and visualised using ECL development solution ab133406.