Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab211093)
Key features and details
- Assay type: Enzyme activity (quantitative)
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Sample type: Cell Lysate, Purified protein, Tissue Lysate
- Sensitivity: 1000 µU
Overview
-
Product name
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
See all ADA kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Sample type
Cell Lysate, Purified protein, Tissue Lysate -
Assay type
Enzyme activity (quantitative) -
Sensitivity
1000 µU -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Mammals, Other species -
Product overview
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab204695) is an assay where inosine formed from the breakdown of adenosine is detected via a multi-step reaction, resulting in the formation of an intermediate that reacts with the ADA convertor and developer to generate uric acid that can be easily quantified at OD293 nm.
The kit measures total activity of Adenosine Deaminase with limit of quantification of 1 mU recombinant Adenosine Deaminase.
-
Notes
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA, EC 3.5.4.4) is an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of adenosine and 2’-deoxyadenosine to inosine and 2’-deoxyinosine. Adenosine Deaminase is widely distributed in various tissues and cells. There are two isoforms, ADA1 and ADA2. ADA1 is widely expressed in most cells in the body, particularly in lymphocytes and macrophages. It is present in the cytosol, nucleus and has been found associated with DPP4/CD26 in the cell membrane. ADA2 was first found in the spleen but is predominantly found in the plasma and serum. Increased serum ADA levels are found in certain infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and various liver diseases such as acute hepatitis, alcoholic hepatic fibrosis, chronic active hepatitis to name a few. Adenosine Deaminase is also a marker for T-lymphocyte proliferation.
Abcam has not and does not intend to apply for the REACH Authorisation of customers’ uses of products that contain European Authorisation list (Annex XIV) substances.
It is the responsibility of our customers to check the necessity of application of REACH Authorisation, and any other relevant authorisations, for their intended uses. -
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 100 tests ADA Assay Buffer (10x) 1 x 25ml ADA Convertor (30 U) 1 vial ADA Developer (10 U) 1 vial ADA Substrate 1 x 500µl ADA Positive Control (50 U) 1 vial Inosine Standard (10 mM) 1 x 100µl U.V. transparent plate (96-well) 1 unit -
Research areas
-
Function
Catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine and 2-deoxyadenosine. Plays an important role in purine metabolism and in adenosine homeostasis. Modulates signaling by extracellular adenosine, and so contributes indirectly to cellular signaling events. Acts as a positive regulator of T-cell coactivation, by binding DPP4. Its interaction with DPP4 regulates lymphocyte-epithelial cell adhesion. -
Tissue specificity
Found in all tissues, occurs in large amounts in T-lymphocytes and, at the time of weaning, in gastrointestinal tissues. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in ADA are the cause of severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell-negative/NK-cell-negative due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADASCID) [MIM:102700]. SCID refers to a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. Patients with SCID present in infancy with recurrent, persistent infections by opportunistic organisms. The common characteristic of all types of SCID is absence of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity due to a defect in T-cell development. ADA-SCID is an autosomal recessive form accounting for about 50% of non-X-linked SCIDs. ADA deficiency has been diagnosed in chronically ill teenagers and adults (late or adult onset). Population and newborn screening programs have also identified several healthy individuals with normal immunity who have partial ADA deficiency. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the adenosine and AMP deaminases family. -
Cellular localization
Cell membrane. Cell junction. Cytoplasmic vesicle lumen. Cytoplasm. Colocalized with DPP4 at the cell junction in lymphocyte-epithelial cell adhesion. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- ada
- ADA_HUMAN
- ADA1
see all
Images
-
Typical inosine standard calibration curve.
-
Kinetic curves showing ADA activity detection in positive control (included in the kit), Jurkat cell lysate (3 µg) and rat brain lysate (19 µg).
-
 ADA Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab211093)Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab211093)
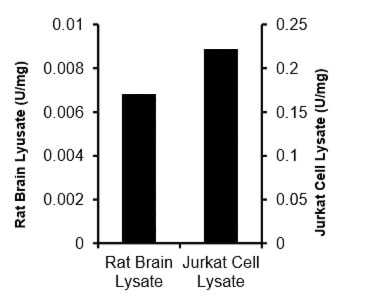
ADA Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab211093)Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab211093)ADA specific activity in rat brain lysate (19 µg) and Jurkat cell lysate (3 µg).










