Recombinant human IL-1 beta protein (Active) (ab259387)
Key features and details
- Expression system: HEK 293 cells
- Purity: > 95% SDS-PAGE
- Endotoxin level:
- Active: Yes
- Suitable for: Cell Culture, SDS-PAGE, Functional Studies, MS, HPLC
Preparation and Storage
-
Alternative names
- Catabolin
- H1
- IFN beta inducing factor
see all -
Function
Potent proinflammatory cytokine. Initially discovered as the major endogenous pyrogen, induces prostaglandin synthesis, neutrophil influx and activation, T-cell activation and cytokine production, B-cell activation and antibody production, and fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. Promotes Th17 differentiation of T-cells. -
Tissue specificity
Expressed in activated monocytes/macrophages (at protein level). -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the IL-1 family. -
Post-translational
modificationsActivation of the IL1B precursor involves a CASP1-catalyzed proteolytic cleavage. Processing and secretion are temporarily associated. -
Cellular localization
Cytoplasm, cytosol. Lysosome. Secreted, exosome. Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome. Secreted. The precursor is cytosolic. In response to inflammasome-activating signals, such as ATP for NLRP3 inflammasome or bacterial flagellin for NLRC4 inflammasome, cleaved and secreted. IL1B lacks any known signal sequence and the pathway(s) of its secretion is(are) not yet fully understood (PubMed:24201029). On the basis of experimental results, several unconventional secretion mechanisms have been proposed. 1. Secretion via secretory lysosomes: a fraction of CASP1 and IL1B precursor may be incorporated, by a yet undefined mechanism, into secretory lysosomes that undergo Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis with release of mature IL1B (PubMed:15192144). 2. Secretory autophagy: IL1B-containing autophagosomes may fuse with endosomes or multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and then merge with the plasma membrane releasing soluble IL1B or IL1B-containing exosomes (PubMed:24201029). However, autophagy impacts IL1B production at several levels and its role in secretion is still controversial. 3. Secretion via exosomes: ATP-activation of P2RX7 leads to the formation of MVBs containing exosomes with entrapped IL1B, CASP1 and other inflammasome components. These MVBs undergo exocytosis with the release of exosomes. The release of soluble IL1B occurs after the lysis of exosome membranes (By similarity). 4. Secretion by microvesicle shedding: activation of the ATP receptor P2RX7 may induce an immediate shedding of membrane-derived microvesicles containing IL1B and possibly inflammasome components. The cytokine is then released in the extracellular compartment after microvesicle lysis (PubMed:11728343). 5. Release by translocation through permeabilized plasma membrane. This may occur in cells undergoing pyroptosis due to sustained activation of the inflammasome (By similarity). These mechanisms may not be not mutually exclusive. - Information by UniProt
Images
-
Fully biologically active when compared to standard. ED50 is ≤ 0.7399 ng /ml, corresponding to a specific activity of 1.35 x 106 units/mg.
-
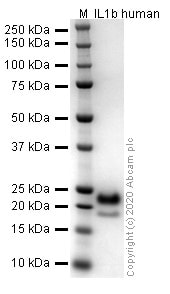
SDS-PAGE analysis of ab259387.
-
Purity: 100%
The spectrum was recorded using a 1260 Infinity II HPLC system with DAD and a MabPac RP column (3.0x100 mm, 4 µm). 5 µL of purified protein was injected and the gradient run from 80 % water:TFA (99.9:0.1 v/v) and 20 % acetonitrile:water:TFA (90:9.9:0.1 v/v/v) to 20 % water:TFA (99.9:0.1 v/v) and 80 % acetonitrile:water:TFA (90:9.9:0.1 v/v/v) within 3 minutes followed by an isocratic step for another 3 min. Flow rate was 0.5 mL/min and the column compartment temperature was 50 °C.
-
M + 1.02 Da (calc mass 17433.98)
The spectrum was recorded with a 6545XT AdvanceBio LC/Q-TOF (Agilent Technologies) and a MabPac RP column (42.1x50 mm, 4 µm, Thermo Scientific). 5 µL of purified protein was injected and the gradient run from 85 % water:FA (99.9:0.1 v/v) and 15 % acetonitrile:FA (90:9.9:0.1 v/v/v) to 55 % water:FA (99.9:0.1 v/v) and 45 % acetonitrile:FA (90:9.9:0.1 v/v/v) within 3 minutes followed by an isocratic step for another 2.5 min. Flow rate was 0.4 mL/min and the column compartment temperature was 60 °C. Data was analysed and deconvoluted using the Bioconfirm software (Agilent Technologies).
-
Human IL-6 concentration was interpolated from the IL-6 standard curve. Supernatants from cell culture samples were serially diluted and assessed by the Human IL-6 ELISA kit (ab178013). Wild-type and IL-6 knockout A549 cells (ab273751) were assessed in duplicate (n=2). Cells were either treated with 20 ng/mL active recombinant human IL-1 beta protein (ab259387) for 24 h to induce expression of IL-6 or not treated with IL-1 beta. Data are represented as the mean and error bars represent standard deviation.
-
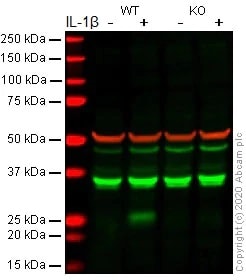
All lanes : Anti-IL-6 antibody [EPR21711] (ab233706) at 1/1000 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A549 Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5ug/ml, 4h) cell lysate
Lane 2 : Wild-type A549 IL-1ß (ab259387) (20 ng/ml, 24h) and Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5 ug/ml for the last 4h) cell lysate
Lane 3 : IL-6 knockout A549 Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5ug/ml, 4h) cell lysate
Lane 4 : IL-6 knockout A549 IL-1ß (ab259387) (20 ng/ml, 24h) and Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5 ug/ml for the last 4h) cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 30 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Observed band size: 25 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 40 kDa (possible non-specific binding)Lanes 1 - 4: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab233706 observed at 25 kDa. Red - loading control ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] observed at 55kDa.
ab233706 was shown to react with IL-6 in wild-type A549 cells in western blot with loss of signal observed in IL-6 knockout cell line ab273751 (knockout cell lysate ab275501). Wild-type and IL-6 knockout A549 cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in fluorescent western blot (TBS-based) blocking solution before incubation with ab233706 and ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 1000 Dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were incubated with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216773) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216776) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.
-
All lanes : Anti-IL-6 antibody [EPR20653] (ab214429) at 1/1000 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A549 Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5ug/ml, 4h) cell lysate
Lane 2 : Wild-type A549 IL-1ß (ab259387) (20 ng/ml, 24h) and Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5 ug/ml for the last 4h) cell lysate
Lane 3 : IL-6 knockout A549 Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5ug/ml, 4h) cell lysate
Lane 4 : IL-6 knockout A549 IL-1ß (ab259387) (20 ng/ml, 24h) and Brefeldin A (ab120299)-treated (5 ug/ml for the last 4h) cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 30 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Observed band size: 25 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?
Additional bands at: 35 kDa (possible non-specific binding)Lanes 1 - 4: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab214429 observed at 25 kDa. Red - loading control ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] observed at 55kDa.
ab214429 was shown to react with IL-6 in wild-type A549 cells in western blot with loss of signal observed in IL-6 knockout cell line ab273751 (knockout cell lysate ab275501). Wild-type A549 and IL-6 knockout cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in fluorescent western blot (TBS-based) blocking solution before incubation with ab214429 and ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 1000 Dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were incubated with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216773) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216776) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.