Human AIF Profiling ELISA Kit (ab126583)
Key features and details
- Sensitivity: 6 µg/ml
- Range: 6 µg/ml - 250 µg/ml
- Sample type: Cell Lysate, Tissue Extracts
- Detection method: Colorimetric
- Assay type: Sandwich (qualitative)
- Reacts with: Human
Overview
-
Product name
Human AIF Profiling ELISA Kit
See all AIF kits -
Detection method
Colorimetric -
Precision
Intra-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Cell lysates 4 3.6% Inter-assay Sample n Mean SD CV% Cell lysates 3 11.4% -
Sample type
Tissue Extracts, Cell Lysate -
Assay type
Sandwich (qualitative) -
Sensitivity
> 6 µg/ml -
Range
6 µg/ml - 250 µg/ml -
Assay duration
Multiple steps standard assay -
Species reactivity
Reacts with: Human
Does not react with: Mouse, Rat -
Product overview
Apoptosis-inducing factor is a mitochondrial enzyme with probable oxidoreductase activity which functions to regulate Complex I activity in the mitochondrial membrane. When mitochondria are damaged, as in apoptosis, AIF can migrate to the cytosol and nucleus. AIF in the nucleus signals chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation. This method of programmed cell death (apoptosis) does not require caspase activation.
In addition to its role in apoptosis defects in AIF1 are the cause of combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency type 6 (COXPD6). COXPD6 is a mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting.
Get results in 90 minutes with Human AIF ELISA Kit (Apoptosis-Inducing Factor 1) (ab184858) from our SimpleStep ELISA® range.
-
Platform
Microplate
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at +4°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 1 x 96 tests 10X AIF Detector Antibody 1 x 1ml 10X Blocking Buffer 1 x 6ml 10X HRP Label 1 x 1ml 20X Buffer 1 x 20ml AIF Microplate (12 x 8 antibody coated well strips) 1 unit Extraction Buffer (ab260490) 1 x 15ml HRP Development Solution 1 x 12ml -
Research areas
-
Function
Probable oxidoreductase that has a dual role in controlling cellular life and death; during apoptosis, it is translocated from the mitochondria to the nucleus to function as a proapoptotic factor in a caspase-independent pathway, while in normal mitochondria, it functions as an antiapoptotic factor via its oxidoreductase activity. The soluble form (AIFsol) found in the nucleus induces 'parthanatos' i.e., caspase-independent fragmentation of chromosomal DNA. Interacts with EIF3G,and thereby inhibits the EIF3 machinery and protein synthesis, and activates casapse-7 to amplify apoptosis. Plays a critical role in caspase-independent, pyknotic cell death in hydrogen peroxide-exposed cells. Binds to DNA in a sequence-independent manner. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in AIFM1 are the cause of combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency type 6 (COXPD6) [MIM:300816]. It is a mitochondrial disease resulting in a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychomotor delay, hypotonia, areflexia, muscle weakness and wasting. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the FAD-dependent oxidoreductase family. -
Post-translational
modificationsUnder normal conditions, a 54-residue N-terminal segment is first proteolytically removed during or just after translocation into the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS) by the mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP) to form the inner-membrane-anchored mature form (AIFmit). During apoptosis, it is further proteolytically processed at amino-acid position 101 leading to the generation of the mature form, which is confined to the mitochondrial IMS in a soluble form (AIFsol). AIFsol is released to the cytoplasm in response to specific death signals, and translocated to the nucleus, where it induces nuclear apoptosis in a caspase-independent manner. -
Cellular localization
Mitochondrion intermembrane space. Mitochondrion inner membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm > perinuclear region. Proteolytic cleavage during or just after translocation into the mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS) results in the formation of an inner-membrane-anchored mature form (AIFmit). During apoptosis, further proteolytic processing leads to a mature form, which is confined to the mitochondrial IMS in a soluble form (AIFsol). AIFsol is released to the cytoplasm in response to specific death signals, and translocated to the nucleus, where it induces nuclear apoptosis. Colocalizes with EIF3G in the nucleus and perinuclear region. - Information by UniProt
-
Alternative names
- AIFM1
- AIFM1_HUMAN
- Apoptosis inducing factor
see all -
Database links
- Entrez Gene: 51060 Human
- Entrez Gene: 9131 Human
- Omim: 300169 Human
- SwissProt: O95831 Human
- Unigene: 424932 Human
- Unigene: 476033 Human
Images
-
Immunocytochemistry analysis of normal untreated HeLa cells with the capture antibody in this kit, ab110327, at 5µg/ml shows staining of AIF is located exclusively to mitochondria. Nuclei were stained with DAPI.
-
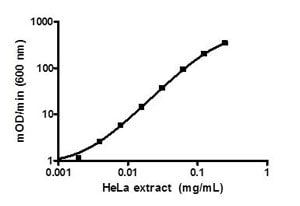
Example serially titrated control sample of HeLa cell extract in the working range of the assay.