D-Amino Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab239721)
Key features and details
- Detection method: Fluorescent
- Platform: Microplate reader
- Sample type: Cerebral Spinal Fluid, Other biological fluids, Saliva, Tissue
Overview
-
Product name
D-Amino Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric) -
Detection method
Fluorescent -
Sample type
Saliva, Other biological fluids, Tissue, Cerebral Spinal Fluid -
Product overview
D-Amino Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab239721) provides a quick, specific and easy method for measuring total D-Amino acid concentrations in a wide variety of samples. In this assay, D-Amino acids are converted into an intermediate by the DAA enzyme mix that will further react with a probe to produce a strong fluorescence signal (Ex/Em= 535/587nm). The kit is simple to use, sensitive and high-throughput adaptable and can detect as low as 1.9 μM of D-Amino acids in biological samples.
-
Platform
Microplate reader
Properties
-
Storage instructions
Store at -20°C. Please refer to protocols. -
Components 100 tests DAA Assay Buffer 1 x 25ml DAA Cofactor 1 vial DAA Developer Mix 1 vial DAA Enzyme Mix 1 vial DAA Probe 1 x 200µl DAA Standard 1 vial -
Relevance
D-Amino acids are present in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. D-Amino acids act as a component of the cell wall in prokaryotes and a neurological regulator in eukaryotes. In mammals, D-Amino acids play an important role in physiological functions and their levels are regulated by D-Amino acid oxidase in the central nervous systems. Some important D-Amino acids include D-serine, D-aspartate and D-alanine. D-serine acts as a modulator of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor, NMDAR), while D-aspartate and D-alanine have been found to be elevated in the white and the gray matter respectively in patients’ brains suffering Alzheimer’s disease. The abnormal levels of D-Amino acids could be used as a marker of neurological diseases: total D-Amino acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been shown to be higher in patients with Alzheimer’s disease when compared to samples from healthy donors.
Images
-
-
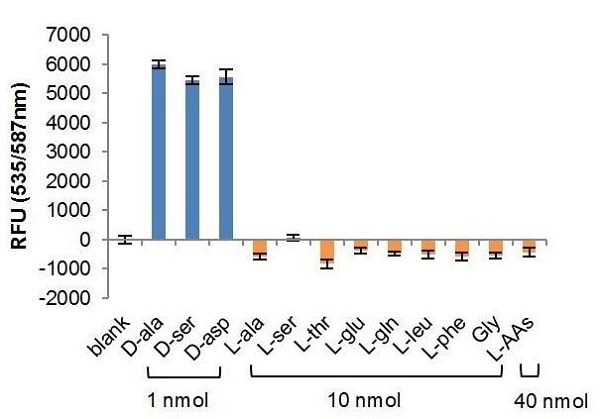
L-Amino acids were tested at a 10-fold molar excess (10 nmol each) and 40-fold molar excess for a mixture od L-amino acids (40 nmol total).
-
D-Amino acid concentrations were 15.4 pmol/µg-protein in rat brain and 4.2 µM in human CSF.